IdentityProviderState
Introduction and overview
The IdentityProviderState AuthState acts as a SAML 2.0 identity provider. It handles the following protocol messages according to the Oasis specification:
- Protocols: authentication request protocol, SingleLogout and ConcurrentLogout (a compatible variant of SingleLogout).
- Binding: HTTP POST (as sender and receiver), HTTP Redirect (as sender and receiver) and HTTP Artifact (as receiver).
Assertions and protocols for the OASIS Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) V2.0: http://docs.oasis-open.org/security/saml/v2.0/saml-core-2.0-os.pdfThe IdentityProviderState can be used to set up a SAML-compliant identity provider that federates authentication information to remote service providers. There is full support for scenarios initiated by identity providers (IdP) as well as by service providers (SP).
By using the SingleLogout protocol, it is also possible to federate logout events. This allows establishing a continuous single sign-on (SSO) space beyond network borders. In particular, servers reachable under unrelated DNS names can be integrated into a single SSO space even though no session cookies can be shared.
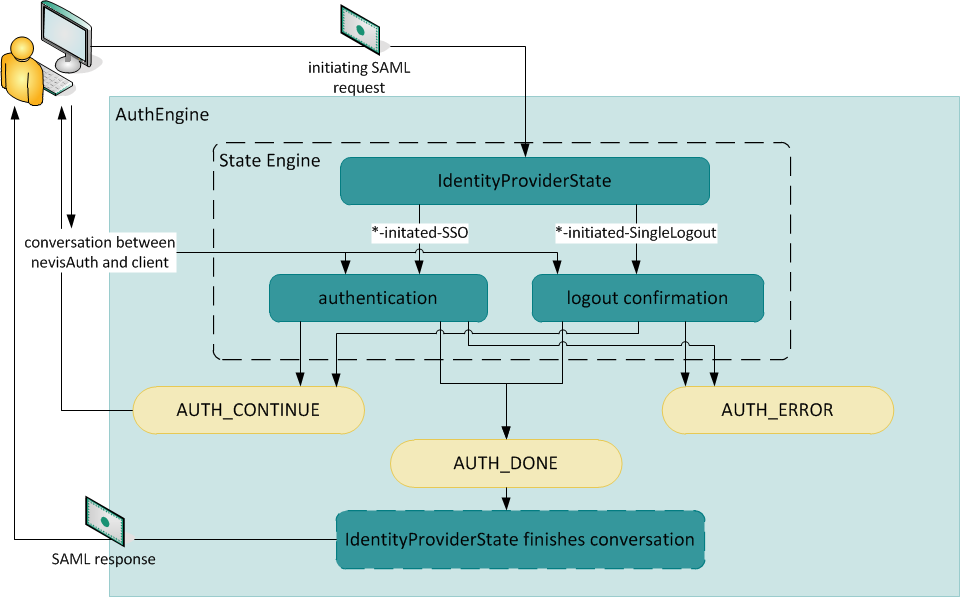
The IdentityProviderState is configured as a dispatcher state, if possible as the first AuthState. It analyzes the incoming SAML messages as well as the state of the session. It then initiates the appropriate SAML protocol by selecting a corresponding transition. The state engine can be configured to handle all operations belonging to the initiated SAML protocol in a straightforward manner.
Once the status AUTH_DONE is reached, the AuthEngine will hand control back to the IdentityProviderState. The IdentityProviderState generates the required SAML messages and initiates the configured SAML binding.
The IdentityProviderState AuthState replaces the Provider AuthState in new setups. The IdentityProviderState is more flexible and more compliant to the SAML 2 specifications. For more information about the Provider AuthState, see chapter Provider SAML 2.0 identity provider.
Logout mechanisms
The SAML specification uses the SingleLogout protocol for logout use cases in federated scenarios. The principle idea of the SingleLogout protocol is that the IdP notifies all SPs participating in a session, one SP at a time. For each SP, the IdP sends out a LogoutRequest message and waits for a LogoutResponse message from that SP. We regard this mechanism as fragile because a problem in one SP can stop the notification chain from reaching all other SPs. In such a case, sessions that should have been closed remain active on some SPs, while other SPs and the IdP have cleared away their sessions for the same client.
As an improvement to SingleLogout, the IdentityProviderState implements an alternative logout mechanism called ConcurrentLogout-Redirect, based on HTTP redirect binding. In the ConcurrentLogout-Redirect mode, when a logout is initiated, the IdP generates LogoutRequest messages for all participating SPs, simultaneously and at once. Each LogoutRequest message is in effect a URL carrying the message in query parameters and pointing to one of the SPs. These URLs are propagated in the OutArg saml.logoutURLs as a comma-separated list. Finally, nevisLogRend embeds the URLs in the final screen of the logout process (typically as hidden iframes), so that all SPs are notified in the background and in parallel. Thus, all SPs receive a LogoutRequest, irrespective of failures at one or several SPs.
From the point of view of an SP, ConcurrentLogout-Redirect behaves exactly like SingleLogout. That is, an IdP running a ConcurrentLogout-Redirect is compatible with any SP operating in SingleLogout mode.ConcurrentLogout is only possible with HTTP redirect binding. It overrides the binding method for outgoing SAML messages (out.binding) for the LogoutRequest message.ConcurrentLogout requires that the LogoutRequest message is received on the logout method. In other words, logout requests to the IdP must be sent with the ?logout query parameter and the IdP must be configured as an entry state for the logout method.Description
The following table describes the characteristics of the AuthState.
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Class | ch.nevis.esauth.auth.states.saml.IdentityProviderState |
| Logging | Saml |
| Auditing | none |
| Properties(generic) | spURL (string, optional)URL of a service provider. Will be used for IdP-initiated scenarios if the IdP does not respond to a SAML request. |
| relayState (string, "${inargs:RelayState}")Source for RelayStates. | |
| logoutMode (string {"SingleLogout","ConcurrentLogout-Redirect"}The protocol in which to notify the SPs participating in the SSO of a logout.*SingleLogoutASingleLogoutprotocol as described in the SAML specification. The IdP notifies one SP at a time with aLogoutRequestand expects to receive aLogoutResponse. In case of SP-initiatedSingleLogout, after all SPs have been notified, a finalLogoutResponseis sent to the initiating SP and the session is invalidated. In case of an IdP-initiatedSingleLogout, the session is marked for invalidation and the transitionLogoutCompleted is selected. * ConcurrentLogout-RedirectThis logout method works like SingleLogout from the point of view of an SP, but all participating SPs are notified in parallel. The IdP constructs LogoutRequests for all SPs at once and encodes the messages into a URL (HTTP redirect binding), so that a LogoutRenderer can embed these URLs in hidden iframes in a logout confirmation screen. The LogoutResponses received from the participating SPs are ignored. For an initiating SP, a LogoutResponse message instead of a LogoutRequest will be encoded in the same fashion. The URLs will be propagated in the outArgs field saml.logoutURLs as a comma-separated list. When implementing concurrent logout, the initial logout request to the IdP must contain the ?logout query parameter so that nevisProxy recognizes the logout method. Otherwise, the IdP session is not invalidated after the LogoutRequests are sent out since there is no processing of the LogoutResponses. | |
| logoutTimeout (time in seconds, 20)This defines the maximum time-to-live for a session after a logout has been initiated. If a distributed logout does not complete before this logoutTimeout runs out, the session is invalidated regardless of its state. | |
| logoutTrigger (string, "${inargs:SAMLLogout:.+:true}")Defines a condition which triggers a logout procedure. The logout process may be cancelled by the cancelTrigger before the first SP notification is sent out, but after that point a logout is inevitable. In the worst case, where a sequence of LogoutRequest/LogoutResponse messages is interrupted, the session will be invalidated after the logoutTimeout has elapsed. | |
| cancelTrigger (string, "${inargs:cancelSAML:.+:true}")Defines a condition that stops an initiated logout, as long as no logout-related messages have been sent to the SPs. Use this trigger in a logout confirmation screen asking the user to confirm his intention to logout. | |
| cancelAction (string, "sendCancelResponse")Defines the action to be taken if the request has been cancelled. Available options are: sendCacelResponse noAction | |
| soap.***in.artifact_sources*out.artifactSourceIdThe properties are used to configure the artifact resolution service binding. See chapter ServiceProviderState for details on the properties. | |
| acsUrlWhitelist.uris (string)This property defines a whitespace-separated list of allowedAssertionConsumerServiceURLsinAuthnRequests. It must be provided to protect the infrastructure against XSS attacks.The property works as follows: If anAuthnRequestcontains an ACS URL, the system searches the whitelist defined here for the ACS URL. If the ACS URL is in the list, the system will use it for the redirection. If the ACS URL is not found, there will be an error. If an AuthnRequest does not contain any ACS URL, the system will ignore the whitelist defined here. In this case, there usually is a value set in the optional property spURL, which will be used as the URL to redirect to. Always set this propertyNote that not setting this property would be equivalent to allowing redirecting to any given URL. If the AuthnRequests contains no ACS URL, the system will use the URL set in the spURL property. However, in case of a malicious AuthnRequest containing an ACS URL of a malicious site, the system will redirect to this malicious URL, if no whitelist is set. Therefore, you should always set a value for this property, even if you do not expect the AuthnRequests to contain any ACS URLs. In this case, it is recommended configuring a whitelist with just one single element, namely the URL you set in the spURL property. This URL is allowed and safe, as it is written in the configuration. |
Configuration examples:
<property name="acsUrlWhitelist.uris"
value="https://nevis.ch/sp1/acs https://nevis.ch/sp2/acs" />
<property name="acsUrlWhitelist.uris" value="${notes:someWhitelist}" />
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Properties(input) | in.bindingin.tolerancein.max_agein.artifact_sourcesin.map_issuer_certificatein.verifyin.prospectVerificationin. keystorerefin.keyobjectref, in.encrypt.*See chapter ServiceProviderState]. When establishing an HTTPS connection, the client will check the hostname in the HTTPS server certificate against the actual server hostname by default. To disable hostname verification, set thesoap.checkHostnameproperty to "false". For more information about the prefix"soap.", see the description of the property*soap.**further above in this table. |
| in.tolerance(int (seconds), 5)Sets the tolerance for time constraints regarding the validation of incoming messages. This value should be set to the maximum expected clock skew between involved servers.When the Identity Provider receives an AuthnRequest, it will validate the IssueInstant of the AuthnRequest by using "in.tolerance + in.max_age". See below for a description of the property in.max_age. | |
| in.max_age(int (seconds), 10)Specifies the maximum time passed since the AuthnRequest was generated (assertion IssueInstant). To disable the max age check, set the property value to "-1" (this is not recommended). | |
| in.assertion(string, -)If set, this assertion will be used for the SAML response instead of a newly generated assertion. | |
| Properties(output) | out.subject (string, "${response:userId}")The subject for which an Assertion is issued. The generated NameID structure can be configured with the following properties:*out.subject.nameQualifier (string, -)* out.subject.spNameQualifier (string, -) *out.subject.format (string, -)* out.subject.spProviderId (string, -) |
| out.oneTimeUse (boolean, "false")Defines whether the oneTimeUse flag should be set in issued assertions. | |
out.binding ({auto, http-post,http-redirect, http-post-deferred, http-redirect-deferred, propagate, internal, internal-assertion}, "http-post")Defines the SAML binding for outgoing SAML messages.The deferred bindings will prepare the necessary data, but instead of initiating the binding right away, will place those values in the following OutArg fields: *nevis.deferred-transfer.destination: The destination of the deferred binding * nevis.deferred-transfer.field.<fieldname>: The request, response and RelayState with field names SAMLRequest, SAMLResponse and RelayState respectively. The internal binding may be used to propagate a SAML message (typically a SAML response) to a back end using nevisProxy's delegation mechanisms. The OutArgs saml.SAMLResponse, saml.SAMLRequest and saml.RelayState will be set if applicable. This binding issues the SAML response immediately and always results in the transition ok.The internal-assertion binding is similar to the internal binding, but instead of issuing a SAML response, only a SAML assertion is generated. It is placed in the OutArg saml.SAMLAssertion. This output binding should be used when issuing SAML assertions as tokens for the SecurityTokenService facade (see chapter Legacy WS-Trust 1.3 SecurityTokenService facade]. This binding issues the SAML assertion immediately and always results in the transition ok.In auto binding, the AuthState will attempt to use the binding of the incoming request. In that case, the configuration should ensure that there is always an incoming SAML request and that the same binding may be used to send the response.As in in.binding, this setting may be further refined by defining different output bindings for different message types. For example: AuthnRequest:http-postLogoutResponse:autoLogoutRequest: http-redirect | |
out.attribute.<name> (string, -)Attributes to be added to generated assertions.Example: <property name="out.attribute.email" value="${sess:emailAddress}" /> / <property name="out.attribute.appId" value="${sess:specialId}" /> | |
out.attributeDelimiter (string, -)If defined, this regular expression will be used to split attribute values. For example, to set a SAML assertion attribute colors with multiple values red, green, indigo, configure the following: <property name="out.attribute.colors" value="red, green, indigo" /> / <property name="out.attributeDelimiter" value=",\s*" /> | |
out.attributeNameFormat.<name> (string, -)If defined, this property sets the name format for the attribute. | |
| out.authnContextClassRef (string, -)The AuthnContextClassRef to set for generated assertions. | |
| out.authnContextDeclRef (string, -)The AuthnContextDeclRef to set for generated assertions. | |
| out.authenticatingAuthority (string, -)The authenticating authority set for generated assertions. | |
| out.sessionTtl ("auto" or int, -)The value can either be auto or an integer that specifies the session time-to-live in seconds.If auto was configured, the time-to-live will be the absolute session time-out specified by the SecToken. The value will be calculated using the initialMaxLifetime set in the session configuration. See chapter Session cache. | |
| out.subjectLocality (string, -)The locality address (IIPv4 or IPv6) or DNS name of the IdentityProvider. | |
| out.audienceRestriction (String, -)Comma-separated list of URIs to add to generated assertions as audience restriction. | |
| out.sessionIndex (string, -)The SessionIndex to set for generated assertions. This is not set by default because Nevis tracks the sessions of authenticated clients using other means. | |
| out.issuerout.sign**out.encrypt.*out.ttlout.keystorerefout.keyobjectref**See chapter ServiceProviderState. | |
| out.sign.hashAlgorithmout.signatureKeyInfo - defines, among others, the signature contents of the assertion. Use this property if you want to include the signature certificate in the assertion.See chapter Common aspects of SAML 2.0 AuthStates. | |
| out.encryption_key_from_expression (string, -)The expression set in this property defines the public key for the encryption of the assertion as a PEM-encoded certificate. The system returns this public key after evaluating the expression. This feature only works with asymmetric encryption. When the encryption key is used by this property, the following properties are ignored: *out.encrypt.keystoreref out.encrypt.keyobjectref. If the matching key cannot be found at runtime or cannot be used (for example, it is no longer valid), the system returns a response with the following status: StatusCode: RequestDeniedStatusMessage*: No valid key | |
| Properties(plug-ins) | in.extensionSee chapter Common aspects of SAML 2.0 AuthStates. |
out.extension.<extension-name> (string, <classname>) <extension-name>.<property-name> (syntax)This syntax specifies plug-ins that will be called to extend outgoing messages. Properties may be passed to the plug-ins using the second syntax shown.Some of these extensions can be considered as advanced feature (like the holder of key extension). Use them only if external parties, such as an external service provider, require you to do so.<extension-name>.methodThe output extender ch.nevis.esauth.auth.states.saml.extensions. SubjectConfirmationExtender adds SubjectConfirmations to generated Assertions. It takes the following properties: Method ofSubjectConfirmation. {bearer,sender-vouches,holder-of-key}. Theholder-of-keyextension is chosen if thex509DataorkeyNameproperty are configured. Otherwise, it defaults tobearer. <extension-name>.x509DataType of X509 reference to the client certificate to insert. Valid values: Certificate, SKI, SubjectName, IssuerSerial. Setting this property will generate a SubjectConfirmation according to the Holder-Of-Key assertion profile. <extension-name>.ttlTime-to-live of theSubjectConfirmation. When this property is set, theNotBeforeandNotOnOrAfterattributes will be generated in accordance with the SubjectConfirmation method. For example, if<extension-name>.methodis "holder-of-key", both attributes are generated; if<extension-name>.methodis "bearer", only theNotOnOrAfterattribute is generated (as the specification forbids specifyingNotBeforein this particular case).<extension-name>.nameIdNameIDvalue to insert into theSubjectConfirmation. TheNameIDstructure can be further configured with the properties<extension-name>.nameId.nameQualifier, <extension-name>.nameId.spNameQualifier, <extension-name>.nameId.formatand<extension-name>.nameId.spProvidedIdas explained forout.subject(see above).<extension-name>.keyNameAKeyNamevalue to insert into theSubjectConfirmation <extension-name>.inResponseTo AnInResponseTovalue to insert into theSubjectConfirmation*<extension-name>.recipientARecipientvalue to insert into theSubjectConfirmation <extension-name>.address AnAddressvalue to insert into theSubjectConfirmation |
Example configuration for the HolderOfKey subject configuration with the client certificate from the transport layer:
<property name="out.extension.HoK"
value="ch.nevis.esauth.auth.states.saml.extensions.SubjectConfirmationExtender" />
<property name="HoK.x509Data" value="Certificate" />
<property name="HoK.ttl" value="15" /> <!-- make it valid only for 15 secs -->
<property name="HoK.inResponseTo" value="${notes:saml.request.id}" />
Alternative example configuration for the HolderOfKey subject confirmation with the keyName field:
<property name="out.extension.HoK"
value="ch.nevis.esauth.auth.states.saml.extensions.SubjectConfirmationExtender" />
<property name="HoK.keyName" value="NevisIDM-X509-Transport" />
<property name="HoK.nameId" value="${sess:altNameId}" />
<property name="HoK.nameId.format" value="https://www.adnovum.ch/nevis/idm/extId" />
<property name="HoK.ttl" value="7200" /> <!-- valid for 2 hours -->
<property name="HoK.inResponseTo" value="${notes:saml.request.id}" />
Example configuration for the Bearer subject confirmation:
<property name="out.extension.Bearer"
value="ch.nevis.esauth.auth.states.saml.extensions.SubjectConfirmationExtender" />
<property name="Bearer.ttl" value="3600" />
<property name="Bearer.inResponseTo" value="${notes:saml.request.id}" />
Example configuration for the sender-vouches subject confirmation:
<property name="out.extension.SV"
value="ch.nevis.esauth.auth.states.saml.extensions.SubjectConfirmationExtender" />
<property name="SV.method" value="sender-vouches" />
<property name="SV.ttl" value="3600" />
<property name="SV.inResponseTo" value="${notes:saml.request.id}" />
Note: the property naming is arbitrary. You may name the property out.extension.bearerSc but it still references the holder-of-key (HoK) extension.
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Methods | process: Initiates SAML protocol according to incoming requests/responses, authentication status of session and evaluation of the logoutTrigger. |
| finish: Generates the SAMLResponse. | |
| handleError: Handles error messages and sends error responses. | |
| Input | All inputs used to resolve SAML bindings according to SAML specification: inargs SAMLRequest, SAMLResponse, RelayState, etc. |
| Transitions | IDP-initiated-SSO: Selected when an authenticated session enters the IdentityProviderState without any incoming SAML request message. |
| SP-initiated-SSO: Selected when an authenticated session enters the IdentityProviderState together with an incoming SAML request message. | |
| IDP-initiated-SingleLogout: Selected when an authenticated session enters the IdentityProviderState without any incoming SAML message, and the condition that triggers a logout procedure is fulfilled (the logoutTrigger applies). Furthermore, the logout mode (logoutMode property) must be set to SingleLogout. | |
| SP-initiated-SingleLogout: Selected when an authenticated session enters the IdentityProviderState together with an incoming logout request. Furthermore, the logout mode (logoutMode property) must be set to SingleLogout. | |
| IDP-initiated-ConcurrentLogout: Selected on the same conditions as the transition IDP-initiated-SingleLogout, but now for the logout mode ConcurrentLogout. | |
| SP-initiated-ConcurrentLogout: Selected on the same conditions as the transition SP-initiated-SingleLogout, but now for the logout mode ConcurrentLogout. | |
| LogoutCompleted: Selected when an IdP-initiated SingleLogout has been completed or when a LogoutResponse has been received after the session has been invalidated. | |
<SAML-protocol>(<remote-issuer>)<remote-issuer>These syntaxes may be used to further fine-tune the configuration relative to specific service providers. The SPs are identified by the issuer of incoming messages, where all forward slashes "/" are replaces by underscores "_". | |
| ok: Selected when no matching transitions with above syntaxes are configured. | |
| invalidAssertionConsumerUrl: Selected when an AuthnRequest contains an AssertionConsumerServiceURL which is not whitelisted. | |
| Output | saml.logoutURLs: In the case of logoutMode ConcurrentLogout-Redirect, this variable will hold a comma-separated list of URLs that transmit LogoutRequests to SPs participating in the SSO. A URL carrying a LogoutResponse to the initiating SP will also be included, if applicable. |
| saml.SAMLRequestsaml.SAMLResponsesaml.RelayStateIf a deferred binding or propagate is configured as output binding, these OutArg variables will contain the SAML messages and, where applicable, a RelayState. | |
| Errors | 99: general error |
| Notes | saml.request. saml.assertion.saml.response.**{*}**See chapter ServiceProviderState. |
| saml.errorCode: Defines the error code to be included in the status code of the SAML response. | |
| saml.errorMessage: Defines the error message to be included in the status message of the SAML response. |
Example
<AuthState name="IdentityProviderDispatcher"
class="ch.nevis.esauth.auth.states.saml.IdentityProviderState"
final="false" >
<ResultCond name="ok" next="AuthDone"/>
<ResultCond name="authenticate:IDP-initiated-SSO" next="StartActualAuthentication"/>
<ResultCond name="stepup:IDP-initiated-SSO" next="AuthDone"/>
<ResultCond name="authenticate:SP-initiated-SSO" next="StartActualAuthentication"/>
<ResultCond name="stepup:SP-initiated-SSO" next="AuthDone"/>
<ResultCond name="IDP-initiated-SingleLogout" next="FederatedLogoutConfirmation"/>
<ResultCond name="SP-initiated-SingleLogout" next="FederatedLogoutConfirmation"/>
<ResultCond name="LogoutCompleted" next="Logout"/>
<Response value="AUTH_ERROR">
<Gui name="AuthErrorDialog"/>
</Response>
<property name="consumerURL" value="https://www.me.com/SAML" />
<property name="spURL" value="https://www.sp.com/SAML" />
<property name="acsUrlWhitelist.uris" value="https://www.sp.com/SAML" />
<property name="logoutTimeout" value="2" />
<property name="logoutMode" value="SingleLogout" />
<property name="in.binding" value="auto"/>
<property name="in.keystoreref" value="Truststore" />
<property name="out.binding" value="LogoutRequest:http-redirect default:http-post"/>
<property name="out.issuer" value="www.me.com-IdP" />
<property name="out.keystoreref" value="Signers" />
<property name="out.keyobjectref" value="Signer" />
<property name="out.attribute.loginid" value="${request.loginId}" />
<property name="out.attribute.email" value="${sess:email}" />
</AuthState>