Appendix H - Deprecation List
This page lists every currently deprecated functionality of nevisProxy, with also a planned removal date. Check regularly if your current configuration is concerned about these planned removals. If one of the below feature is still used in your setup, then there is also a deprecation notice in the navajo log file, either during startup or during incoming request. If you are affected, adapt your configuration by using a replacement or contact support if you depend on the deprecated functionality.
ServerAdmin attribute of the Server tag
Replacement: no replacement
Deprecated since: 5.2.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
The SSLRequire attribute of the SSL tag
Replacement: in general replaced by the Require expression by Apache.
Deprecated since: Before LTS19
Plan to remove: version 9.x
The Protocol parameter of the HttpConnectorServlet
Replacement: no replacement
Deprecated since: 8.2405.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
The Loglevel attribute of the Server tag
Replacement: Use LogLevel instead
Deprecated since: 8.2405.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
The AwaitingResponse parameter of the HttpConnectorServlet
Replacement: no replacement
Deprecated since: 8.2405.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
The LegacyRegexpMatching parameter of the HttpConnectorServlet
Replacement: no replacement
Deprecated since: 8.2405.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
The CheckAlwaysClientCert parameter of the IdentityCreationFilter and SecurityRoleFilter
Replacement: no replacement
Deprecated since: 8.2411.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
- Type: boolean
- Usage Constraints: optional, basic feature
- Default:
false - If the client presents a certificate during the first login request, then there is a check to confirm that the same certificate is present during subsequent requests.
This check can be disabled by setting the attribute to
false.
The H2SerializeHeaders attribute of the H2 tag in navajo.xml
Replacement: no replacement
Deprecated since: 8.2411.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
ch.nevis.navajo.SessionCleanupWaitTimeout
Replacement: use ch.nevis.navajo.ListenerWaitTimeout instead
Deprecated since: 8.2411.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
Type: Integer
Unit: msec
Default: 30000
The maximal time to wait for a reaper-call, before shutting down an instance.
ch.nevis.isiweb4.auth.ExternalHint
Replacement: use request:reauthenticate() instead
Deprecated since: 8.2411.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
Attribute recognized by the IdentityCreationFilter. May be used to temporarily lock an authenticated session in a Lua script. Example:
request:setAttribute("ch.nevis.isiweb4.auth.ExternalHint", "lock")
org.apache.request.ParsedUri
Replacement: The parameter AllowEncodedSlashes may be used instead
Deprecated since: 8.2411.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
Type: Boolean
Default: true
If set to true, this parameter decodes the encoded URI of an incoming request for internal nevisProxy processing. For example the parameter turns the URI /UIFont%20CMSStyle.swift into /UIFont CMSStyle.swift, as %20 stands for ' '.
If set to false, the parameter does not modify anything and forwards the undecoded URI unchanged.
This parameter is directly related to the parameter URLEncoding of the servlet HttpConnectorServlet. The URLEncoding parameter encodes the outgoing URI from nevisProxy to the back-end application. We highly recommend setting both parameters to true. If your setup requires one of the parameters to be false, set the other one to false too, on all HttpConnectorServlets. The parameter URLEncoding can also be set to false centrally by adding the code line ch.nevis.isiweb4.servlet.connector.http.URLEncoding=false to the bc.properties configuration file.
The Lua request method getRequestUri
Replacement: Use the method getRequestPath instead
Deprecated since: 8.2411.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
Returns the URI of the request. The URI consists of the context path, the servlet path and the path info, if given.
The Lua request method setRequestUri
Replacement: Use the method setRequestPath combined with setQuery instead
Deprecated since: 8.2411.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
Sets the URI of the request. Only use this method for modifying the request URI of a side call request, as the modification of the original request's URI may result in undefined behavior.
request:setRequestUri("/set/side/call/uri")
The Lua request methods getContextPath and setContextPath
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2505.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
getContextPath()
Returns the context path on which the web.xml is mapped (see navajo.xml).
setContextPath(path)
Overwrites the context path; the overwritten context path is visible to all filters mapped after this LuaFilter.
The value client-side of the ProxyPolicy parameter in the HttpConnectorServlet
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2505.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
client-side: The proxy acts as a client-side proxy for HTTP.
The commands nevisproxy genrules nevisproxy whitelist and the practices URI whitelisting and Self-learning of input validation
Replacement: Use the ModSecurityFilter instead
Deprecated since: 8.2505.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
URI whitelisting
A whitelist of all allowed URIs (path portion) may be generated based on existing access.log files. These rules are used to restrict access to known handlers of the application only, and may be used in addition to the parameter whitelisting described in the previous section, Self-learning of input validation. The following example demonstrates a shell script which generates/updates a request path whitelisting.
#!/bin/sh
PATH=/usr/bin:/bin:/opt/nevisproxy/bin
# the OPTIONS variable controls the rule generation, enter "nevisproxy default genrules"
# for a list of available options
OPTIONS="-h"
# PFX is the name (path portion) of your application
PFX="appl"
# this sample script uses the "default" proxy instance
# the log file contains all relevant URIs and is used every time you update the rules
LOG=/var/opt/nevisproxy/default/logs/$PFX.log
# the rule db file contains the URI pattern you may edit
DB=/var/opt/nevisproxy/default/logs/$PFX.db
TMP=$DB.tmp
# filters the access.log file by the defined application path /$PFX cat /var/opt/nevisproxy/default/logs/access.log | \
cut -d ' ' -f 7 | cut -d '?' -f 1 | grep "^/$PFX/" > $LOG.tmp
touch $DB
touch $LOG
cat $LOG >> $LOG.tmp
nevisproxy default genrules -i $LOG.tmp -c $DB $OPTIONS > $TMP
rm -f $LOG.tmp
grep "# ADD line " $TMP | cut d ' ' -f 5 > $LOG
grep "^QS_PermitUri +QSF" $TMP > $DB
rm -f $TMP
echo "ch.nevis.isiweb4.filter.validation.$PFX.Description=generated for /$PFX"
echo "ch.nevis.isiweb4.filter.validation.$PFX.BlockOnError=true"
echo "ch.nevis.isiweb4.filter.validation.$PFX.DecodingRules=URL_decode_unicode"
echo "ch.nevis.isiweb4.filter.validation.$PFX.RegexpType=PCRE"
cat $DB | awk '{print substr($0, 27, length($0)-27)}' | \
awk -F'"' '{ print "ch.nevis.isiweb4.filter.validation..URIWhiteList." NR-1 "=" $2}'| \
sed -e "s::$PFX:g"
Such a script may be executed multiple times until it has learned all possible URIs and the output (stdout) can be added to the customer profiles to be mapped to the application which has been defined by the PFX variable within the script profile, see the chapter "Managing custom profiles.
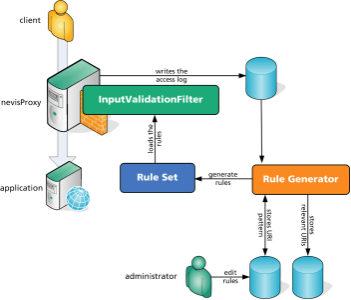
Self-learning of input validation
The InputValidationFilter provides a learning mechanism to generate the ParameterRules patterns, which are used to protect an application.
This learning mechanism is based on two components:
- The first component is an audit log that contains the data transferred from clients to the server. This audit log is generated by the InputValidationFilter that has been mapped to the application's URL.
- The second component is a rule generator that processes the audit log data and creates ParameterRules rules matching the captured data.
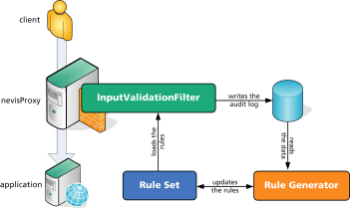
The following steps are necessary to learn a new rule set:
- Add an InputValidationFilter and map it to the URL of the application. Configure the audit.log facility of the filter. You also need to specify the decoding you want to apply to the incoming data. It is important to use exactly the same decoding during the learning phase that you are going to use later when the rules are enforced.
Example filter configuration:
<filter>
<filter-name>SelfLearningValidationFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>ch::nevis::isiweb4::filter::validation::InputValidationFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>AuditLog.FileName</param-name>
<param-value>/var/opt/nevisproxy/<instance_name>/logs/test_input_audit.log</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>AuditLog.PassPhrase</param-name>
<param-value>${exec: cat /var/opt/neviskeybox/default/public/node_keypass}</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>DecodingRules</param-name>
<param-value>URL_decode_unicode</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>SelfLearningValidationFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/appl/servlet/</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
- Run the rule generator multiple times, for example every hour. The rule generator processes the audit log as well as the existing rules and updates them. Repeat this process multiple times (usually for several days) until the rules do not change anymore.
You can invoke the rule generator with the nevisproxy whitelist command, which has the following syntax:
Usage:
nevisproxy <instance> whitelist <application> <passphrase> <audit log> <rule file> ['utf8'] ['varnames']
Options:
application: name of the rule set to generate
passphrase: the passphrase to decrypt the data (or a program writing the passphrase to stdout)
audit log: audit log file to read the collected data from
rule file: rule file to read/write the generated rules
utf8: enables utf8 multibyte character support
varnames: generates ParameterRules rules with variable parameter names
The next code block gives an example of the nevisproxy whitelist command:
nevisproxy siven whitelist test-profile some_pwd /var/opt/nevisproxy/siven/logs/test_input_audit.log /var/opt/nevisproxy/siven/conf/profile.properties varnames
The command generates a file called profile.properties. This file contains the profile "test-profile" with parameter rules based on the content of the test_input_audit.log file:
# profile 'test-profile' implementing input validation
# statistics 'rule.'<id>'='<name>':'<total updates>':'<total hits>' '<updates>':'<hits>
# rule.0=test_param_1:2:18 0:6
# rule.1=test_param_2:2:18 0:6
# rule.2=test_param_3:1:4 0:2
ch.nevis.isiweb4.filter.validation.test-profile.Description=input validation, generated Mon Apr 20 13:32:08 2020, 0 updates
ch.nevis.isiweb4.filter.validation.test-profile.BlockOnError=true
ch.nevis.isiweb4.filter.validation.test-profile.RegexpType=PCRE
ch.nevis.isiweb4.filter.validation.test-profile.ParameterRules.0=test_param_1:^[a-zA-Z0-9]{6,13}$:allow:silent
ch.nevis.isiweb4.filter.validation.test-profile.ParameterRules.1=test_param_1:.*:deny
ch.nevis.isiweb4.filter.validation.test-profile.ParameterRules.2=test_param_2:^[a-zA-Z0-9]{8,31}$:allow:silent
ch.nevis.isiweb4.filter.validation.test-profile.ParameterRules.3=test_param_2:.*:deny
ch.nevis.isiweb4.filter.validation.test-profile.ParameterRules.4=test_param_3:^[\?]{0,1}$:allow:silent
ch.nevis.isiweb4.filter.validation.test-profile.ParameterRules.5=test_param_3:.*:deny
ch.nevis.isiweb4.filter.validation.test-profile.ParameterRules.6=.*:.*:allow:log
- Once the rules no longer change after you invoked the rule generator, you can upload the profile into the InputValidationFilter (the audit log configuration is no longer necessary):
<filter>
<filter-name>SelfLearningValidationFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>ch::nevis::isiweb4::filter::validation::InputValidationFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>Profile</param-name>
<param-value>test-profile</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
- Restart the proxy instance and monitor the navajo.log file. Update the rule set if there are any false rule violations (false positives) within the navajo.log file.
Where does the InputValidationFilter learn?
The InputValidationFilter learns rules by activating the audit log either within a production or test environment:
| Environment | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Production | - You can invoke the rule generator until there are no further updates to the rules. - You can directly activate the new profile.- The generator can learn from real data that provides an accurate rule set. | - There is the risk of learning rules from invalid user input or even from an attempted attack. |
| Test | - There is no risk of learning rules from an invalid pattern or potential attack. | - You need to define extensive test patterns to learn from. - You need to test the generated profile in the production environment in permissive mode (BlockOnError=false). |
The helper tool qsfilter2
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2505.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
Rule generator. Creates QS_Permit directives and rule patterns from audit log files.
The helper tool wlsg
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2505.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
Internal binary for rule generation for the self-learning feature of input validation.
The helper tool qsrotate
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2505.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
Log rotation tool similar to Apache's rotatelogs.
The helper tool qssign
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2505.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
A log data integrity check tool. It reads log data from stdin (pipe) and writes the signed data to stdout adding a sequence number and signature to every log line. qssign.rb is a Logstash filter plug-in that you can use to verify the signatures of log messages in real time.
The helper tool qstail
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2505.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
Shows the end of a log file beginning at a defined pattern.
The helper tool qsgrep
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2505.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
Searches a file for a pattern and prints the data in a new format.
The helper tool qsexec
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2505.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
Command execution triggered by patterns within log files.
The helper tool qscheck
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2505.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
Monitor tool testing the TCP connectivity to servers used by mod_proxy.
The helper tool qshead
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2505.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
A utility that reads from stdin and prints all lines to stdout until reaching the defined pattern.
The helper tool qsdt
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2505.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
Simple tool to measure the elapsed time between related log messages.
The helper tool ipfilter
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2505.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
Simple tool to replace/hide IP addresses in log files.
The MQServlet
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2505.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
A connector where any POST body will be sent as an MQ message to the defined broker. This servlet can be either used like any normal servlet (i.e., REST clients) and/or with side calls from LuaFilter scripts.
ch::nevis::nevisproxy::servlet::sink::MQServlet
libSinkServlet.so.1
Configuration
BrokerURI
Type: string
Usage Constraints: required, basic
Defines the broker uri. See the official documentation of activeMQ for more information. Example: tcp://your.broker.ch:61616
TargetURI
Type: string
Usage Constraints: required, basic
Define target name of queue or topic. Example: my.example.uri
Username
Type: string
Usage Constraints: required, basic
Define the username for accessing the broker.
Password
Type: string
Usage Constraints: required, basic
Define the password for accessing the broker.
Type
Type: enum
Usage Constraints: optional, basic
Default: Topic
Define target type, possible values are "Queue" or "Topic".
The methods getVersion/setVersion of the Cookie Lua Object
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2511.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
cookie:getVersion()
Up to version 8.2505.x.y:
- Returns the version of the cookie as a number.
Starting from version 8.2511.x.y:
- Returns always
0.
cookie:setVersion(versionAsNumber)
Up to version 8.2505.x.y:
- Sets the version of the cookie.
Starting from version 8.2511.x.y:
- This call will be ignored.
The version attribute of the ResponseCookie parameter in the RewriteFilter
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2511.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
Up to version 8.2505.x.y:
- The ResponseCookie parameter can contain the following rule:
[:version:<regex>:remove]
Starting from version 8.2511.x.y:
- The rewriting of the
versionin the ResponseCookie parameter will be ignored.
The undocumented action passthrough of the parameter ErrorPolicy in the EncryptionFilter
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2511.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
The parameter CookieManager.PassthroughParsed in the CookieCacheFilter
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2511.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
Type: boolean
Usage Constraint: optional
Default: true
If set to "true", the cookies that are allowed to be passed through will be parsed and serialized according to RFC 6265.
The undocumented url-mapping suffix
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2511.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
generalResourceDir attribute of the Engine tag of navajo.xml
Replacement: no replacement
Deprecated since: 8.2511.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
You can use the attribute generalResourceDir to configure a directory. If this directory contains a file with the name navajo_style_sheet.css, the system will use it as style sheet. A file with the name Nevis_f2.gif is used as a GIF file. These two resources are referenced in every HTML response generated by the server. If the system cannot find one of these resources in the configured directory, it it will use the compiled resource.
useStyleSheet attribute of the Engine tag of navajo.xml
Replacement: no replacement
Deprecated since: 8.2511.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
Set this attribute to "true" to restore original behavior. The following nevisProxy components reference the style sheet: DeflateFilter, StatusServlet, LoginRendererServlet if the built-in login page will be rendered.
Support for not RFC 7512 conform PKCS11 URLs
Replacement: use RFC 7512 conform PKCS11 URLs
Deprecated since: 8.2511.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
PKCS#11 object specification strings
When interacting with a PKCS#11-compatible HSM, nevisProxy references its content with a PKCS#11 object specification string.
In order to load the PKCS#11-compatible OpenSSL engine provided by nevisProxy you have to add those lines into the env.conf file:
OPENSSL_ENGINES=/opt/nevisproxy/lib/engines
export OPENSSL_ENGINES
The PKCS#11 object specification strings are similar but not identical to the corresponding PKCS#11 URLs defined in RFC-5712.
PKCS#11 OBJECT SPECIFICATION STRING
PKCS#11 object specification strings are distinguished from
PEM files by its 'pkcs11:' protocol prefix. Following the
'pkcs11:' protocol prefix are name/value pairs describing
PKCS#11 library, objects, or object access behavior (caching
etc).
Sample:
pkcs11:library=./libcryptoki.so&dologin=true&keep=true&cache=true&tokenlabel=one&objectlabel=seven&pinenv=PKCS11_PIN1
library
Specify PKCS#11 library. This may be an absolute
filename or a relative filename (in which case
LD_LIBRARY_PATH should be appropriately set). The
library filename is typically libcryptoki.so.
dologin
Specify login behavior. Setting it to 'true' forces a
login into the PKCS#11 token (after opening sessions).
Some token objects may only be accessible if logged in.
The tool will try to log into the token anyway, if the
token indicates 'login-required' thru its information
flags.
cache
This option will reuse token information. Useful if e.g.
both private key and matching certificate are used.
keep
This option will keep PKCS#11 sessions and login states.
tokenlabel
Specify label of the token carrying the object in
question.
slotnumber
Is an alternative to tokenlabel.
objectlabel
Specify label of the object in question.
objectid
Is an alternative to objectlabel. Note that object ids
are often not intended to be human readable (e.g. just
20 random bytes).
pinenv
Specify the name of the environment variable that
contains the pin used to log into the PKCS#11 token. If
this option is not specified then the environment
variable that contains the pin is assumed to be
PKCS11_PIN.
This option is useful if your objects are distributed on
several tokens that are protected by different pins.
pinenvironmentvariable
Same as option pinenv.
pinfile
Specifies the file name containing the PIN used to log in to the PKCS#11 token. Only the first line is read, without the terminating '\n'..
A configuration for HSM-based certificates within the navajo.xml file using the SSLCertificateKeyFile attribute may look like this:
pkcs11:library=/opt/nevisproxy/lib/libctreinitwrap.so.1&dologin=true&keep=false&cache=false&tokenlabel=daytona&objectlabel=Server
When you use the above configuration string in an XML-based configuration (as attribute value), the character & needs to be replaced by &.
To find out the value of the various options, use the PKCS#11 (Cryptoki) interface and utility. See: Appendix E. To test the PKCS#11 OBJECT SPECIFICATION STRING, use the provided libnevisproxypkcs11engine library in combination with the storeutl method of OpenSSL.
Getting a certificate from HSM
If a certificate is needed out of the HSM, use the provided libnevisproxypkcs11engine library in combination with the storeutl method of OpenSSL. The sample command in the next code block shows you how:
/opt/nevisproxy/bin/openssl storeutl -engine /opt/nevisproxy/lib/libnevisproxypkcs11engine.so -noout -text 'pkcs11:library=/usr/local/primus/lib/libprimusP11.so&dologin=true&objectlabel=proxy.cert&type=cert&pinenv=PKCS11_PIN'
The output of the sample command above is as follows:
This is a public symbol
engine "libnevisproxypkcs11engine" set.
PKCS#11 User PIN for Slot 0 (PRIMUS X-Series):
0: Certificate
Certificate:
Data:
Version: 3 (0x2)
Serial Number:
.....
You can also define one of the following environment variables (usually defined in the file env.conf):
PKCS#11 LIBRARY ENVIRONMENT VARIABLES
The PKCS#11 library supports the following environment
variables:
PKCS11_CACHE_PRIO
This prioritized environment variable indicates to reuse
token information. Useful if e.g. both private key and
matching certificate are used. This environment variable
has precedence over the environment variable
PKCS11_CACHE and over the option 'cache' of the
corresponding PKCS#11 object specification string.
PKCS11_CACHE
Indicates to reuse token information. Useful if e.g.
both private key and matching certificate are used. This
environment variable is ignored if either the
environment variable PKCS11_CACHE_PRIO is set or if the
option string.
PKCS11_KEEP_PRIO
This prioritized environment variable indicates to keep
PKCS#11 sessions and login states. It has precedence
over the environment variable PKCS11_KEEP and over the
option 'keep' of the according PKCS#11 object
specification string.
PKCS11_KEEP
Indicates to keep PKCS#11 sessions and login states.
This environment variable is ignored if either the
environment variable PKCS11_KEEP_PRIO is set or if the
option 'keep' is set in the corresponding PKCS#11 object
specification string.
PKCS11_PIN
Specifies a default pin used to log into the PKCS#11
token. Used in combination with the environment variable
PKCS11_PIN_ENVIRONMENT_AHEAD and/or the environment
variable PKCS11_PIN_ENVIRONMENT.
By specifying the option pinenv in your PKCS#11 object
specification string and assigning an environment
variable name to it you can override this default pin by
another pin.
This is useful if your objects are distributed on
several tokens that are protected by different pins.
PKCS11_PIN_ENVIRONMENT
Specifies whether to check if a (single) pin is provided
in the environment variable PKCS11_PIN (or in the
environment variable specified by the option pinenv in
the according PKCS#11 specification string). This check
is only done if the environment variable
PKCS11_PIN_ENVIRONMENT_AHEAD is not set and if the
according pin getter failed. It is of use in the cases
where the process has disconnected from its controlling
terminal and /dev/tty is no longer valid.
PKCS11_PIN_ENVIRONMENT_AHEAD
Specifies whether to check if a (single) pin is provided
in the environment variable PKCS11_PIN (or in the
environment variable specified by the option pinenv in
the according PKCS#11 specification string). This check
is done before the according pin getter is called. It is
of use in the cases where the process has disconnected
from its controlling terminal and /dev/tty is no longer
valid. Besides it may be of use to suppress the
multiplicity of pin prompts.
Securosys, frontend connections: Configure navajo.xml using the OpenSSL engine
To adjust the file navajo.xml proceed as follows:
In the SSL tag of the file navajo.xml, configure the parameters SSLCertificateFile and SSLCertificateKeyFile as follows:
SSLCertificateFile="pkcs11:library=/usr/local/primus/lib/libprimusP11.so&dologin=true&objectlabel=<the label>&type=cert&pinenv=PKCS11_PIN&cache=false"
SSLCertificateKeyFile="pkcs11:library=/usr/local/primus/lib/libprimusP11.so&dologin=true&objectlabel=<the label>&type=privkey&pinenv=PKCS11_PIN&cache=false"In the Server tag of the file navajo.xml, configure the parameter SSLCryptoDevice as follows:
SSLCryptoDevice="pkcs11"
Add the following code block to the file env.conf:
PKCS11_PIN=...
export PKCS11_PIN
PKCS11_PIN_ENVIRONMENT_AHEAD=true
export PKCS11_PIN_ENVIRONMENT_AHEAD
OPENSSL_ENGINES=/opt/nevisproxy/lib/engines
export OPENSSL_ENGINESYou can now restart the proxy.
The Nevis PKCS11 Cryptoki Wrapper
Replacement: none
Deprecated since: 8.2511.0
Plan to remove: version 9.x
Description
PSTOK5 WRAPPER SOFTTOKEN ENVIRONMENT VARIABLES
The pstok5 wrapper softtoken, a cryptoki reinit wrapper, has
been developed to overcome some of the PKCS#11 constraints.
It supports threadsafeness, reinitialization after fork,
cryptoki session reuse after forking and signal safeness.
You enable the cryptoki reinit wrapper library
(libctreinitwrap) by specifying it as option 'library' in
the PKCS#11 object specification string. The actual cryptoki
library you want to use should then be specified in the
environment variable PKCS11_LIBRARY.
The following environment variables are supported by the
pstok5 wrapper softtoken:
PKCS11_BLOCKSIGNALS
Specifies whether to block most signals while in PKCS#11
calls.
Sample: PKCS11_BLOCKSIGNALS=true
PKCS11_LIBRARY
Specifies the PKCS#11 library (libcryptoki) to be
proxed.
Sample: PKCS11_LIBRARY=.../libcryptoki.so
PKCS11_REINIT
Specifies whether to try to re-init PKCS#11 library on
fork.
Sample: PKCS11_REINIT=true
PKCS11_SAVESESSION
Specifies whether to save (shield) cryptoki sessions.
Sample: PKCS11_SAVESESSION=true
PKCS11_SERIALIZETHREADS
Specifies whether to serialize threads.
Sample: PKCS11_SERIALIZETHREADS=true
PKCS11_FORCE_INITIALISATION
Calls the C_Finalize/C_Initialize methods if the
C_Initialize function call returns
CKR_CRYPTOKI_ALREADY_INITIALIZED ensuring that the
library get reinitialized.
Sample: PKCS11_FORCE_INITIALISATION=true
PKCS11_RETRY_AUTO_RECOVERY
Library tries to recover from device errors if the
C_Sign function call returns a "device error" by doing
a reinitialization.
Sample: PKCS11_RETRY_AUTO_RECOVERY=true
You may configure these variables within the nevisProxy instance's env.conf file. The following example defines the vendor's PKCS 11 library as well as several options to enable fault tolerance:
PKCS11_LIBRARY=/usr/lunasa/lib/libCryptoki2_64.so
export PKCS11_LIBRARY
PKCS11_SAVESESSION=true
export PKCS11_SAVESESSION
PKCS11_REINIT=true
export PKCS11_REINIT
PKCS11_FORCE_INITIALISATION=true
export PKCS11_FORCE_INITIALISATION
PKCS11_RETRY_AUTO_RECOVERY=true
export PKCS11_RETRY_AUTO_RECOVERY
Tracing:
to enable tracing, you have to set the following tracegroups:
if used on the frontend (navajo.xml):
BC.Tracer.DebugProfile.NavajoSSL=4
if used on the backend (HttpsConnectorServlet, BackendConnectorServlet):
bcx.net.debug.host=all
bcx.net.debug=handshake,record,ssl
BC.Tracer.DebugProfile.OpenSSLHandshk=4
BC.Tracer.DebugProfile.OpenSSLRecord=4
BC.Tracer.DebugProfile.OpenSSLStream=4