HttpConnectorServlet
The HttpConnectorServlet forwards HTTP requests to content providers using HTTP over TCP/IP. It supports load balancing and special handling of proxy-unaware content providers (content rewriting for HTML) as well as security features (cookie management).
All its configuration attributes may also be used for the HttpsConnectorServlet (see the chapter "HttpsConnectorServlet").
Classname:
ch::nevis::isiweb4::servlet::connector::http::HttpConnectorServlet
Library:
libHttpConnectorServlet.so.1
Profile:
JavaScript-Parsing: Regular expressions for some common JavaScript constructs containing URLs.
Configuration
| InetAddress | address list; required, basic connectivity | Sets a whitespace-separated list of INET addresses (<host>:<port>, where <host> may be an IP address or a host name). All backends must be on a single line and separated with blank spaces. Failsafeness will work only if several server names are configured. The first server name is used as the ‘primary’ server (the one where all requests are sent to if load balancing is not enabled).
It is possible to define load balancing groups. Each group will be "|" separated. For example: ip1:p1 ip2:p2 | ip3:p3 ip4:p4.
In such a load balancing setup, the selection of the backend server depends on the following criteria:
1. The backend server must be part of the defined load balancing group (in the above example, this is the group with servers ip1 and ip2);
2. The backend server must not be marked as "bad".
The proxy makes its final selection of the back-end server from among the available backend servers according to the Round Robin principle. The proxy then stores the assignment of the client session to the selected backend server, thus binding this frontend/backend to the session. All further requests within this session are now sent to the same backend server.
In the case that the backend server has a problem, the proxy returns the request to the user together with an HTTP code 502. Also, the proxy removes the assigned backend server from the session. In place of the old server, the proxy selects a new backend server from the same load balancing group for all further user requests within this session. All the time, the session remains active and valid.If there is no functioning backend server available in the first load balancing group, the proxy selects an appropriate backend server from the second load balancing group, according to the previously described selection criteria. In our example, the second group contains the servers ip3 and ip4.
You can also set a dynamic address with the following syntax:
<source>:<name>;[<source>:<name>;]...
<source: ENV, AUTH, HEADER, PARAM, or SESSION. <br/> <name>: the name in the given source
i.e. SESSION:host;. This will get the host to connect to the attribute "host" in the session. You can set exactly one dynamic address (without any other address).
If IP addresses are used, Hostname may need to be set.
You can also specify a YAML file, (file:///var/opt/nevisproxy/<your instance name>/work/WEB-INF/connection.yml) which you can change on the fly. Read more about YAML configuration in the chapter below.
The file-modification of the YAML file will be checked in the interval configured under periodicity in the Timer section in the file navajo.xml. |
| MappingType | enum: requesturi, pathinfo; optional, basic connectivity; default: requesturi | Configures the part of request path that will be sent to the content provider: requesturi: the complete URI of the incoming request will be sent to the content provider; pathinfo: the pathinfo will be sent to the content provider. requesturi = servlet mapping + pathinfo |
| AutoRewrite | string array; optional, troubleshooting; default: header | This attribute configures rewriting policies for non-proxy aware content in the HTTP/HTML response. It may be set to a newline or white space separated list of the following values:
redirect: the HTTP header ‘Location’ will be re-written
cookie: the HTTP header ‘Set-Cookie’ will be rewritten (path information)
body: HTML tags will be rewritten only in response to bodies of type ‘text/html’.
header: alias for ‘redirect’ and ‘cookie’
on: alias for ‘header’ and ‘body’
off: neither the headers nor the body of the response are rewritten.
Rewriting of the response body may only be omitted if the content provider is proxy aware. See ‘HostName’ attribute for more information about content rewriting.
If "cookie" is enabled for AutoRewrite and the mappingTyp is "pathinfo", the path of the cookie is rewritten in the same way that an absolute URI is written in the response body. In other words, the path will be prefixed with the servlet-path. |
| URIPrefix | string (absolute URI); optional, advanced | This attribute configures the entry point of the content provider. The behavior of this attribute depends on the attribute MappingType: MappingType=pathInfo: the configured URIPrefix will be prepended to the pathInfo; MappingType=requestURI: the configured URIPrefix will be prepended to the requestURI; requestURI = servlet mapping + pathinfo
For a more detailed description, see chapter: Managing the URL namespace. |
| URIPrefix.trailingSlashRedirect | boolean; optional, advanced; default: false | Defines how to handle the URI /<URIPrefix>. If set to 'true', it will be treated like /<URIPrefix>/. |
| CookieManager | string array; optional, basic; default: retain:^JSESSIONID$ allow:^.*$ | This attribute configures the caching of cookies coming from the content provider. A cookie cached by the CookieManager is not forwarded to the browser, but merged into each incoming request before propagated to a content provider. You set the mode of the CookieManager as follows: <rule>:<regexp>
The following rules are allowed:
store: The CookieManager stores the cookie sent by the content provider within nevisProxy (the client does never receive the cookie and cannot send one either). "store" is a suitable option if the connector is used for unprotected and protected content at the same time.
retain: If a session exists, the CookieManager stores the specified cookie ("store"). Otherwise, it sends the cookie to the client ("allow").
block: The CookieManager blocks (that is, ignores) any cookie sent by the content provider or the client.
allow: The CookieManager allows the cookie sent by the content provider or client to pass through if there is no matching "store" or "block" rule.
The regular expression is optional. If not configured, all cookies match. The default regex-type is "PCRE(da)". Cookies that do not match any rule are blocked. Use the next configuration to disable the CookieManager:<param-value>off</param-value>. A disabled CookieManager prevents the logout call from sending any cookie to the content provider.To find out which cookies are set by content providers, either enable cookie warnings in your browser, or enable NavajoOp tracing (NavajoOp=1) and monitor Set-Cookie HTTP headers.
Examples: store:^JSESSIONID$; store:^Navajo$; allow:^.*Language$; block:^.*Session.*$
Cookies that do not match any rule are blocked.
Use the next configuration to disable the CookieManager: <param-value>off</param-value>. A disabled CookieManager prevents the logout call from sending any cookie to the content provider.
To find out which cookies are set by content providers, either enable cookie warnings in your browser, or enable NavajoOp tracing (NavajoOp=1) and monitor Set-Cookie HTTP headers. |
| CookieManager.CookieBinding | enum: none, resource, mapping; optional, advanced; default: none | Defines the scope of a stored cookie:
- none: cookie is used for each individual access to the servlet instance.
- resource: Like none, but if multiple resources are configured for load balancing, the cookie is not shared between the resources.
- mapping: All mappings of this servlet have their own set of cookies. |
| CookieManager.DefaultCookiePath | string; optional, advanced; default: / | The cookie path to set if the backend sets no path. |
| LogoutURI | string array; optional, basic feature; default: off | This attribute allows notifying the content provider about the termination of a session, to also terminate the application session.
The syntax of this attribute is: <uri>(:<header>)*. For example in /logout/path:User-Agent:Date:
<uri>: Describes the URI to be used for the notification call (through a GET request).
<header>: Specifies the names of the header fields to be delegated with the termination request (such as the header fields "User-Agent" and "Date" in the previous example). The <header> part is optional. If an optional header does not have a value, the header will not be sent with the request.
The session listener is required to trigger the notification when a session termination occurs. For more information about the session listener (also SessionListener), see: Session listener. |
| LogoutURI.Interception | string; optional, advanced; default: off | Configures the behavior when a client requests the URI configured in the "LogoutURI" parameter. The following actions can be taken upon such a request:
- <url>: An URL to redirect to.
- auto: A redirect to the same location as requested will be triggered with an appended "logout" url parameter.
- off: Default, no specific action will be taken and the request will be forwarded to the backend server. |
| LogoutURI.NumberOfThreads | integer optional, advanced min: 0, max: 100, default: 0 | Number of threads to start to send the logout-call in separate threads. This will avoid to block the session-reaper |
| LogoutURI.MaxNumberOfQueuedLogoutRequests | integer; optional, advanced; min: 1, max: 100000, default: 1000 | Maximal number of queued logouturi-requests. This value will only be used if 'LogoutURI.NumberOfThreads' is > 0. If this limit is reached, all following logouturi-requests will either be ignored (LogoutURI.Blocking=false), or will be called in blocking mode (LogoutURI.Blocking=true). |
| LogoutURI.Blocking | boolean; optional, advanced; default: true | If the limit set by LogoutURI.MaxNumberOfQueuedLogoutRequests is reached, all following logouturi-requests will either be ignored (LogoutURI.Blocking=false), or will be called in blocking mode (LogoutURI.Blocking=true). |
| LoadBalancing | boolean: true, false; optional, basic feature; default: false | Activates load balancing. Load balancing will work only if several server names are configured in InetAddress. Load balancing is sticky, based on client session. To change this, set ‘ResourceManager’ accordingly. |
| DisableBindingStatusCode | string, conditional; optional, advanced; default: not set, failover disabled | This attribute enables failover and defines the status code(s) for the content provider that failed. It is not set by default. The connector first returns the response with the special status code before it removes the binding (from the HttpConnectorServlet configuration). |
| ResourceManager | string; optional, advanced; default: ch::nevis::isiweb4::servlet::connector:: base::SessionResourceManager | Configures the classname of the used resource manager. The following resource managers are available:
- ch::nevis::isiweb4::servlet::connector::base::SessionResourceManager: Per-session round-robin load balancing (session sticky).
- ch::nevis::isiweb4::servlet::connector::-base::StatelessResourceManager: Per-request round-robin load balancing (no stickiness). See also: reference guide, the chapter Fail-safety and load balancing. |
| ResourceHint | string; optional, advanced | This attribute defines a numeric value, which is used as an index of a backend resource. Indexing starts at "1". Thus, this attribute allows direct access to a specific backend resource in case load balancing is enabled.
The selected backend resource is made persistent with the resource manager. You define the resource manager with the ResourceManager attribute. It is not possible to use this attribute together with a stateless resource manager (StatelessResourceManager, see also the ResourceManager attribute). |
| ResourceHint.Sticky | boolean; optional, advanced; default: false | Makes the backend selected with ResourceHint in a load-balanced group sticky. The default is false. |
| ResourceHint.RemoveFromQuery | boolean; optional; default: false | If this attribute is set to "true", the system removes the resource hint from the query that is sent to the backend. |
| ResourceManager.RetryTimeout | integer (sec); optional, advanced; default: 10; and if only one backend is set, and CheckForMultipleIPAddresses is false, the default is 0 | Configures the retry timeout of the resource manager. Raise this timeout, if probing the backend takes a very long time (e.g., the server is stopped, network infrastructure does not immediately signal an ‘unreachable destination’ and the ConnectTimeout cannot be lowered to, e.g., less than 2 seconds). Disable it (by setting it to 0) to avoid subsequent 502 errors, when the first was caused by a long-running transaction (e.g., generating a report) but the backend is not generally affected by performance problems. |
| ResourceManager.RetryBindingTimeout | integer (sec); optional, advanced; default: 7200 | Defines the time after which the connector will retry to bind the resource to a session. |
| ResourceManager.WatchURI | string; optional, advanced | Defines a URI to call to check if a service is available or not. If not configured, only a TCP connect is done to check availability of a backend. If a URIPrefix is set, this prefix will be prepended to the given “ResourceManager.WatchURI”. |
| ResourceManager.WatchStatusCode | integer; optional, advanced; min: 100 / max: 600 | The expected HTTP status code when the ResourceManager.WatchURI is called. If the status code does not match the one configured, the backend is considered as unavailable. |
| ResourceManager.WatchTimeout | integer (msec); optional, advanced; min: 0 / max: 3600000 | The request timeout for the call to ResourceManager.WatchURI. If the backend did not answer within the configured timeout, the backend will be considered as unavailable. |
| ResourceManager.NoSessionCookie ResourceManager.NoSessionCookie. | | The attributes ResourceManager.NoSessionCookie and `ResourceManager.NoSessionCookie.define the NoSessionCookie feature. <br/> For a description of the NoSessionCookie feature, see: NoSessionCookie. <br/> For a description of theResourceManager.NoSessionCookie.` attributes, see the table: NoSessionCookie configuration, on the bottom of this page. |
| ResourceManager.FailoverThresholdCount | integer; optional, advanced; default: 1 | The number of requests that shall need to fail before a particular backend is considered defective. Increase this to prevent a failover if an otherwise healthy backend occasionally fails to satisfy isolated requests. The threshold setting is shared by all the resources configured for the servlet, the actual failure counters are maintained independently per backend.
Until the failure counter reaches the configured threshold, the backend continues to be considered available. The configured ResourceManager will only proceed to consider other resources once the threshold has been reached. If a ResourceManager.WatchURI is configured, the ResourceManager.FailoverThresholdCount will be ignored. |
| ResourceManager.FailoverThresholdCountLifeTime | integer (sec); optional, advanced; min: 0, max: 604800, default: 0 (expiration disabled) | The validity period of the failed request counter. Once the configured time has passed since the last failed request to the backend, the counter is reset to zero. |
| ResourceManager.DisablePing | boolean; optional, advanced; default: false; and if only one backend is set, and CheckForMultipleIPAddresses is true, the default is false. | This disables ping on startup and on retry. |
| RequestTimeout | integer (msec); required, scaling; default: 120000 (2 min) | The TCP timeout, in milliseconds, for the reading of the response from the web server. |
| ConnectTimeout | integer (msec); required, scaling; default: 15000 (15 sec) | Timeout in milliseconds to open the TCP connection to the content provider. Lower this timeout for fast recovery (in conjunction with a short ‘ResourceManager.RetryTimeout’). Raise this timeout if your server has networking problems and the proxy receives ‘connection refused’ errors, even though the server is up, running, and responding to connect requests. |
| KeepAlive | boolean: true, false; required, scaling/tuning; default: false, secure default: true | Pool TCP connections for later reuse. If set to "false", the connection is closed after use, and a new TCP connection will be established for the next request. The web server should support keepalive in an acceptable range. If this is not the case, keepalive should be disabled. |
| KeepAlive.LifeTime | integer (sec); required, scaling; default: 600 | The absolute lifetime of a TCP connection if connection pooling is enabled (see KeepAlive above). The connection is closed when:
time(now) - time(connect) >= KeepAliveLifeTime
This parameter is of interest when a firewall between nevisProxy and a content providers drops the TCP connection. |
| KeepAlive.ConnectionPoolSize | integer; required, scaling; min: 0, max: 604800, default: 50 | With the config attribute ’KeepAlive.ConnectionPoolSize’ the number of pooled TCP connections can be configured. A TCP connection is only put in the pool if it does not exceed the configured size. |
| KeepAlive.InactiveInterval | integer; required, scaling; default: 60 | With the KeepAliveInactiveInterval, it is possible to establish an upper limit for the http session cache at runtime. If a backend sends 'max=0' in a 'keep-alive' response, the connection will be closed. If the backend sends its own 'timeout' in a 'keep-alive' connection, this timeout will overwrite the 'KeepAlive.InactiveInterval' of the HttpConnectorServlet. |
| KeepAlive.ByClient | boolean; optional, advanced; default: false | If KeepAlive is set to true, the TCP connection will only be reused for the same client. A call from a different client will use another TCP connection from the connection pool.
Restriction: TLS caching per session (SSLCache=on) and connection pooling by client (KeepAlive.ByClient=true) is not supported. |
| KeepAlive.RetryOnFail | boolean; optional, advanced; default: true | A risk involved in keep-alive requests is that the backend closes a connection just before the proxy wants to reuse this connection. If you set this attribute to "true", nevisProxy will try to open a new connection in such a situation. |
| BlockSize | Integer (byte); optional, advanced; min: 1, max: 524288, default: 8192 | The block size used for reading/writing.(Advanced configuration, as a rule, the default value should be just fine.) |
| Poll | boolean; optional, advanced; default: false | If this attribute is set to "true", the system forwards the request and response body without caching. This is needed for the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) and Outlook Anywhere, which both use RPC over HTTP.
Do not map any buffering filters if the Poll attribute is set to "true". Otherwise, the error HTTP-0081 will occur. Buffering filters are, for example, rewrite and validation filters. |
| Protocol | enum: HTTP/0.9, HTTP/1.0, HTTP/1.1; optional, troubleshooting; default: not set, browser protocol | This attribute configures the protocol version. If not set, the one on the browser request will be used. |
| DelegateHeader | string array; optional, basic feature; default: no delegation | This attribute configures additional (constant) HTTP header fields: <header name>:<header value> For dynamic header propagation, see the chapter: Invalidate a session after a SingleRequest using the LuaFilter. |
| SuppressHeader | string; optional, advanced; default: no suppression | A space-separated list of (case-insensitive) HTTP header fields that will be suppressed when the request is sent to the content provider. |
| UniqueIdHeaderName | string optional, advanced | Deprecated This attribute is deprecated. Instead, use a DelegationFilter directly mapped on the HttpConnectorServlet. Delegate the following header: ENV:bcx.servlet.request.TransferID:transferId.This attribute configures how to call the header field which contains the uniqueId. If not set, no header with the uniqueId will be set. As uniqueId the transferId is used. |
| OutboundProxy | address; optional, advanced | A single INET address (<host>:<port>, where <host> may be an IP address or a host name) that specifies a forward HTTP proxy to use. |
| OutboundProxyAuthorization | string; optional, advanced; default: none | Credentials <username>:<password> for creating the proxy authorization header. |
| OutboundProxy.ErrorCodes | string; optional, advanced; default: 502,503,504 | A list of numerical HTTP status codes that signal that the forward proxy is unable to reach a host. Only required for insecure (plain HTTP) forward proxies. |
| DNSCache | boolean; optional, troubleshooting; default: true | Without DNS caching, the DNS name is resolved for every request. You will need to disable this setting if the IP address of your host can change, e.g. if you do failover switching using DNS.
If you turn off this attribute (DNSCache) and enable the attribute KeepAlive, your backend may behave incorrectly if the DNS switches while a connection is being pooled in the HttpConnectorServlet. For example, the backend may not understand the received session cookies like JSESSION, because the DNS switched the underlying IP of a given name. |
| DNSCache.ttl | integer; optional; min: 1 / max: unlimited; default: 3600 | If the attribute DNSCache is set to "true", this attribute (DNSCache.ttl) specifies the time period in seconds to cache the DNS info, before the system will retrieve the IP address again. |
| HostName | string; optional, advanced; default: Hostname of first element in InetAddress | Defines the HTTP header field Host to send to the content provider. If not set, the host part of the corresponding address in the InetAddress field is used.
You usually need to set this attribute, if you have both a failsafe setup with multiple addresses in the InetAddress field and content rewriting enabled (in the AutoRewrite attribute). If the content provider sends a URL with a host part, and the HTTP "Host" header is not considered, auto-rewriting does not work properly: Redirects or links will directly point to the content provider instead of the issue used.
Notes regarding the configuration of the HostName attribute:
- It is possible to configure several values for this attribute (’ ’- or ’\n’-separated). Every value is assigned to the respective value ofInetAddress.
- If this attribute is not configured, the system uses the host part of the InetAddress value for the host part of fully qualified URLs.
- If the attribute's configuration only contains one value, the system will assign this value to all values of theInetAddressattribute.
- If failsafeness groups have been defined in the InetAddress attribute, the HostName attribute must contain the same number of groups.
- If each failsafeness group defined in the InetAddress attribute has the same amount of inet addresses, a HostName attribute value with the same amount of hosts is valid as well.
- Optionally, it is possible to specify the port using the notation <hostname>:<port>.
- It is possible to define variables from the ENV and AUTH context. E.g., ENV:HTTP_Host;. This makes it possible to use the "Host" header sent by the client.
- If both the LogoutURI parameter and a dynamic hostname are specified (by using ENV, AUTH or similar), the system sends the value of the InetAddress attribute as "Host" header on the logout request to the backend. |
| HostName.StripDefaultPort | boolean; optional, advanced, conditional; Supported pragmas: break; Default: true | Defines if the default port should be stripped. If set to false, the \'Host\' header always contains the assigned port number. |
| HostName.StripNonDefaultPort | boolean; optional, advanced, conditional; Supported pragmas: break; Default: false | Defines if ports which are not 80 or 443 should be stripped. If set to false, the \'Host\' header always contains the assigned port number. |
| ProtocolExtension | enum: none, webdav optional, basic feature default: nonedeprecated: use AllowedMethods, instead | Deprecated This attribute is deprecated. Use the attribute AllowedMethods instead.This attribute configures which HTTP protocol extensions are enabled.Currently, the following values are supported:none: means no extension, supported methods are: GET, POST, HEAD, DELETE, TRACE, CONNECT, OPTIONS, PUTwebdav: additional methods are: MERGE, UNCHECKOUT, MKACTIVITY, PROPPATCH, LOCK, CHECKOUT, SEARCH, COPY, MKCOL, MKWORKSPACE, PROPFIND, UPDATE, REBIND, BASELINE-CONTROL, UNBIND, CHECKIN, VERSION-CONTROL, UNLOCK, LABEL, MOVE, ACL, BIND, REPORT |
| ProxyPolicy | enum: stealth, via-header, mime-completion, client-side, commit-response, commit-response-disabled; optional, advanced; default: stealth | This attribute supports configuration of proxy behavior in a space- or newline-separated list that may contain the following values:
- via-header: Enables setting the ‘via’ response header so that the client can detect whether the HTTP status came from the proxy or from the content provider.
stealth: Suppress ’via’ response header.
- mime-completion: If the 'Content-Type' header of the response is not set, a header with the configured mime-type mapping will be set (workaround for buggy content providers).
- commit-response: The response is committed in any case. This prevents the response from being overwritten by a subsequent component (e.g. an ErrorFilter or similar).
- commit-response-disabled: The response is not committed in any case. This ensures that the response can be overwritten by any subsequent component.
- client-side: The proxy acts as a client-side proxy for http.
Configuration settings:
ProxyPolicy stealth (default)
ProxyPolicy via (add ’via’ header to HTTP response as specified by RFC2616) |
| ResponseLineSize | integer (byte); optional, security, scaling; min: 512, max: 524288, default: 4096 | The maximum allowed line size in the HTTP header of the response. |
| SetServerHeader | boolean; optional, advanced security; default: false | If true, the ‘server’ HTTP header of the response will be passed to the client, exposing internal information to the client. |
| URLEncoding | boolean; optional, troubleshooting; default: true | If set to "true" (which is the default), this attribute encodes forbidden characters in the outgoing URI from nevisProxy to the back-end application. For example, if "true", the attribute changes the URI /UIFont CMSStyle.swift into /UIFont%20CMSStyle.swift. This feature can be useful for the integration of content management systems (CMS) that use URLs with forbidden characters.
This attribute is directly related to the low-level attribute org.apache.request.ParsedUri of the servlet container (see the chapter: Low-level properties). The org.apache.request.ParsedUri attribute decodes an encoded URI of an incoming request for internal nevisProxy processing. We highly recommend setting both attributes to "true".
Note: You can set the attribute URLEncoding to "false" centrally. To do this, add the following code lines to the bc.properties configuration file:
-ch.nevis.isiweb4.servlet.connector.http.URLEncoding=false: This code line sets the attribute URLEncoding to "false" for all HttpConnectorServlets and HttpsConnectorServlets, unless it is explicitly overwritten in the servlet itself.
-ch.nevis.isiweb4.servlet.connector.http.HttpConnectorServlet.URLEncoding=false: This code line sets the attribute URLEncoding to "false" for all HttpConnectorServlets, unless it is explicitly overwritten in the servlet itself.
-ch.nevis.isiweb4.servlet.connector.http.HttpsConnectorServlet.URLEncoding=false: This code line sets the attribute URLEncoding to "false" for all HttpsConnectorServlets, unless it is explicitly overwritten in the servlet itself.
-ch.nevis.isiweb4.servlet.connector.websocket.URLEncoding=false: This code line sets the attribute URLEncoding to "false" for all WebsocketServlets, unless it is explicitly overwritten in the servlet itself.
The file bc.properties is usually located under /var/opt/nevisProxy/<instance name>/conf/bc.properties. |
| ResponseRewrite.ParsingMode | enum: strict, tolerant; optional, advanced; default: strict | Sets parsing to either "tolerant" or "strict". If parsing mode is set to ’strict’, the HTML parser tries to parse improper HTML with heuristics. It finds any URLs in a text/html body and (if activated, see below) performs further replacements on any inline javascript or css parts as if they were inside a text/css or text/javascript body. For the regular expression replacement, the "strict" parsing mode makes errors terminate the whole parsing process. |
| ResponseRewrite.IgnoreInlineCSS | boolean; optional, advanced; default: false | Disables parsing/processing of inline CSS blocks in HTML content. |
| ResponseRewrite.IgnoreInlineJS | boolean; optional, advanced; default: false | Disables parsing/processing of inline JavaScript blocks in HTML content. |
| ResponseRewrite.IgnoreHTML-Comments | boolean; optional, advanced; default: true | Disables parsing of HTML comments. |
| ResponseRewrite.PostProcessingURLRegexps | string array; optional, advanced | A newline-separated list of regular expressions for the configuration of additional post-processing for URL rewriting. Works like ResponseRewrite.JavaScriptRegexps and ResponseRewrite.StyleSheetRegexps and permits identification of additional URLs in any content defined in ResponseRewrite.PostProcessing.ContentTypes. The default regex-type is "PCRE(da)". |
| ResponseRewrite.PostProcessing.ContentTypes | string; optional, advanced; default: ^text/ | A newline separated list of regular expressions which defines the content types on which the ResponseRewrite.PostProcessingURLRegexps applies. The default regex-type is "PCRE(da)". |
| ResponseRewrite.PostProcessingDelimiters | string array; optional, advanced; default: 10,13 (\n \r) | Supports configuration of alternative delimiters for the tokenization of the response body for Response-Rewrite.PostProcessingURLRegexps. Response-Rewrite.PostProcessingURLRegexps is the only rewriting that supports specification of delimiters, all other ResponseRewrite options tokenize by line or statement (\';\').
The configured regexp (ResponseRewrite.Post-ProcessingDelimiters) is executed on the resulting tokens of the body. Delimiters must be configured as a whitespace- or \',\'-separated list of decimal ascii characters. |
| ResponseRewrite.PostProcessing-IgnoreQuotes | boolean; optional, advanced; default: true | Ignores single and double quotes for tokenizing during post-processing. If quoting is active (ResponseRewrite.PostProcessingIgnoreQuotes=false), text inside matching quotes is ignored. This includes the other type of quote as well as escaped quotes. Quotes can be escaped with a backslash. |
| ResponseRewrite.PostProcessing-CaseInsensitive | boolean; optional, advanced; default: true | Makes regular expressions in ResponseRewrite.PostProcessingURLRegexps case-insensitive. |
| ResponseRewrite.ContentTypes. | string; optional, advanced | A newline-separated list of regular expressions which defines the given ContentType. E.g., ContentTypes.json=^application/json. For each '' at least the ContentType..rules has to be defined.
Defaults are:
- html: ^text/html, ^application/xhtml
- css: ^text/css
- javascript: ^text/javascript, ^application/javascript, ^application/x-javascript |
| ResponseRewrite.ContentType..rules | string; optional, advanced | Defines a list of regular expressions for identifying URLs inside the given content type. The default regex-type is "PCRE(da)". The system will ignore this parameter if the content type is "html" (ResponseRewrite.ContentType.html.rules). To enable the evaluation of the rules for content type HTML, set the parameter ResponseRewrite.ContentType.html.rules.enabled (see below). |
| ResponseRewrite.ContentType.html.rules.enabled | boolean; optional, advanced; default: false | If this parameter is set to "true", the system will also evaluate the parameter `ResponseRewrite.ContentType..rules for content type HTML (ResponseRewrite.ContentType.html.rules). <br/> When you configure the parameter ResponseRewrite.ContentType..rulesfor HTML, keep in mind that there are already some built-in HTML rules. If you add these built-in rules to the configuration ofResponseRewrite.ContentType.html.rules`, the system will rewrite the URLs twice. These targets are rewritten automatically: HREF, SRC, ICONSRC, ACTION, BACKGROUND, CODEBASE, CODE, IMAGEPATH, LOWSRC, and ARCHIVE |
| ResponseRewrite.ContentType..rules.ignoreQuotes | string; optional, advanced | Ignores quotes as parenthesis around a string or similar inside the given ContentType code. |
| ResponseRewrite.ContentType..separators | string; optional, advanced | Defines the line-separators inside the given ContentType. |
| ResponseRewrite.MaxMatchLen | integer; required, advanced; default: 2048 | Maximum length of a string a regular expression rule may match. The amount of memory needed for response rewriting grows with the configured value. For performance reasons, the maximum should be kept as low as possible. When set to zero, there is no limit to the length of a matched URL. Such a setting is not recommended. |
| AwaitingResponse | boolean; optional, advanced; default: true | If set to 'true', the response of the content provider will not be awaited. Set 'AwaitingResponse' to 'false' for "sidecalls" done in rewrite-rules such as `^/(.)$:/$1:S=NotifierServlet:continue. |
| RewriteBufferSize | integer (bytes)optional, adnvanceddefault: 16384 bytes | The size of the internal buffer (in bytes) for buffering HTML tags. Only relevant if the response is rewritten (see AutoRewrite). |
| AllowedMethods | string; optional, advanced | With this parameter, a comma- or white-space-separated list of all allowed HTTP methods can be defined. You can also specify one of these method groups: <br/> - **ALL-WEBDAV:** all webdav methods can be addressed <br/> - **ALL-HTTP:** all HTTP methods can be addressed <br/> Additionally, you can forbid methods included in "ALL-WEBDAV" or "ALL-HTTP", by specifying the method to be forbidden with a -` sign in front of it. For example:
ALL-WEBDAV, ALL-HTTP, -CHECKIN means that all HTTP and WEBDAV methods are allowed, except "CHECKIN".
With the parameter AllowedMethods, you configure the HTTP methods allowed by nevisProxy, to connect to the backend. This in contrast to the allowedMethods attribute of the web application configuration, with which you configure the HTTP methods allowed by the front end, to connect to nevisProxy. When you modify the AllowedMethods parameter described here, you may also have to adapt the allowedMethods attribute of the web application configuration. For a description of the allowedMethods attribute, see chapter: 4.1.4.2 Web applications.
Per default the following methods are allowed: GET, POST, HEAD, DELETE, TRACE, CONNECT, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH
- ALL-WEBDAV methods are: MERGE, UNCHECKOUT, MKACTIVITY, PROPPATCH, LOCK, CHECKOUT, SEARCH, COPY, MKCOL, MKWORKSPACE, PROPFIND, UPDATE, REBIND, BASELINE-CONTROL, UNBIND, CHECKIN, VERSION-CONTROL, UNLOCK, LABEL, MOVE, ACL, BIND, REPORT.
- ALL-HTTP methods are: GET, POST, HEAD, DELETE, TRACE, CONNECT, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH. |
| MergeResponseHeaders | boolean; advanced; default: true | If set to "true" (default), this parameter merges response headers with the same name, as described in RFC 2616. |
YAML configuration
Place the path to the yaml configuration in the HttpConnector InetAddress parameter by starting with file:// i.e.(file:////ms.adnovum.ch//var//opt//nevisproxy//default//work//WEB-INF//connector1.yml)
The root element must be host-groups containing at least one host-group element. The host-group must at least contain one address element which holds one single address (name or IP). Optionally you can also specify the host name right after the address element with a host-name element, which will be set as the host header. The host-name can also be before a host-group element which then specifies the default host name for that group, which still can be overwritten by a host-name element inside the host-group.
Host groups do a fail-over as soon all specified hosts in that group are not accessible. Inside a host group the hosts are load-balanced.
You also can have custom based elements in the yaml file for your own purposes. Those elements can be anywhere in the yaml configuration and must be prefixed with "custom-" to avoid future name clashes.
host-groups:
- host-name: my.host.de
- host-group:
- address: 192.168.1.3
- address: 192.168.2.3
- address: 234.123.1.10
host-name: special.host.ch
- host-name: other.host.de
- host-group:
- address: 168.13.10.3
- host-group:
- address: 172.16.4.10
- host-name: some.host.org
- custom-id: 1.2.3.4.5.6
AutoRewrite Capabilities
The AutoRewrite parameter provides some standard use cases where you do not need a RewriteFilter. Neverthless it comes with some restrictions and some well-known flaws where you have to correct the outcome of the AutoRewrite with a RewriteFilter.
With pathinfo
AutoRewrite can handle absolute and relative URLs as well as port numbers in the hostnames of the absolute URL. It cannot rewrite a relative path without leading slash "index.html", for this you currently need a RewriteFilter. The AutoRewrite also doesn't support path normalization of /../../index.html.
Example
For all examples the connector is mapped on /example
- The Location header is /custom/index.html the AutoRewrite will transform this correctly to /example/custom/index.html.
- The Location header is custom/index.html the AutoRewrite will not be rewritten at all but should be /example/custom/index.html.
- The Location header is /../index.html the AutoRewrite will transform this to /example/../index.html, but should be /index.html (no normalizing).
Cookie path
The cookie path AutoRewriting doesn't rewrite path=/, but should rewrite it to pathinfo. If a sub path is set, it just replaces the path with the pathinfo but doesn't add the sub path.
Example
For all examples the connector is mapped to /example
- Set-Cookie path=/ is not rewritten at all, but should be path=/example
- Set-Cookie path=/any/thing is rewritten to path=/example, but should be path=/example/any/thing
- Set-Cookie path=/prefix/custom with URIPrefix /prefix should be rewritten to path=/example, but should be path=/example/custom
Referrer header
AutoRewrite do not rewrite the Referrer header.
Performance decrease with UrlEncryptionFilter
If the AutoRewrite parameter is set and auto-rewriting is "on", the HttpConnectorServlet sends the body back in different little chunks. This can slow down the UrlEncryptionFilter.
To avoid this, add a buffering LuaFilter to the filter chain as workaround. The buffering LuaFilter collects all chunks up to a certain size, then sends everything back in bigger chunks. Map the LuaFilter in between the UrlEncryptionFilter and the HttpConnectorServlet. For this case, you can use the LuaFilter_buffering.example configuration, which you can find in the installed nevisproxy package in "/opt/nevisproxy/examples/various/LuaFilter_buffering.example".
NoSessionCookie
The NoSessionCookie feature of the Http(s)ConnectorServlet allows you to implement sticky load balancing without creating real sessions in nevisProxy. Instead of storing the information in the session, an encrypted cookie is sent to the client. This cookie contains all state details of the given Http(s)ConnectorServlet. This is possible because the HttpConnectorState is externalized, encrypted, then signed, and finally added as a response cookie header. When the client sends back the NoSessionCookie with the next request, the Http(s)ConnectorServlet verifies, decrypts and reads the cookie, thus being able to retrieve such state details as the connected backend or the notification URI:
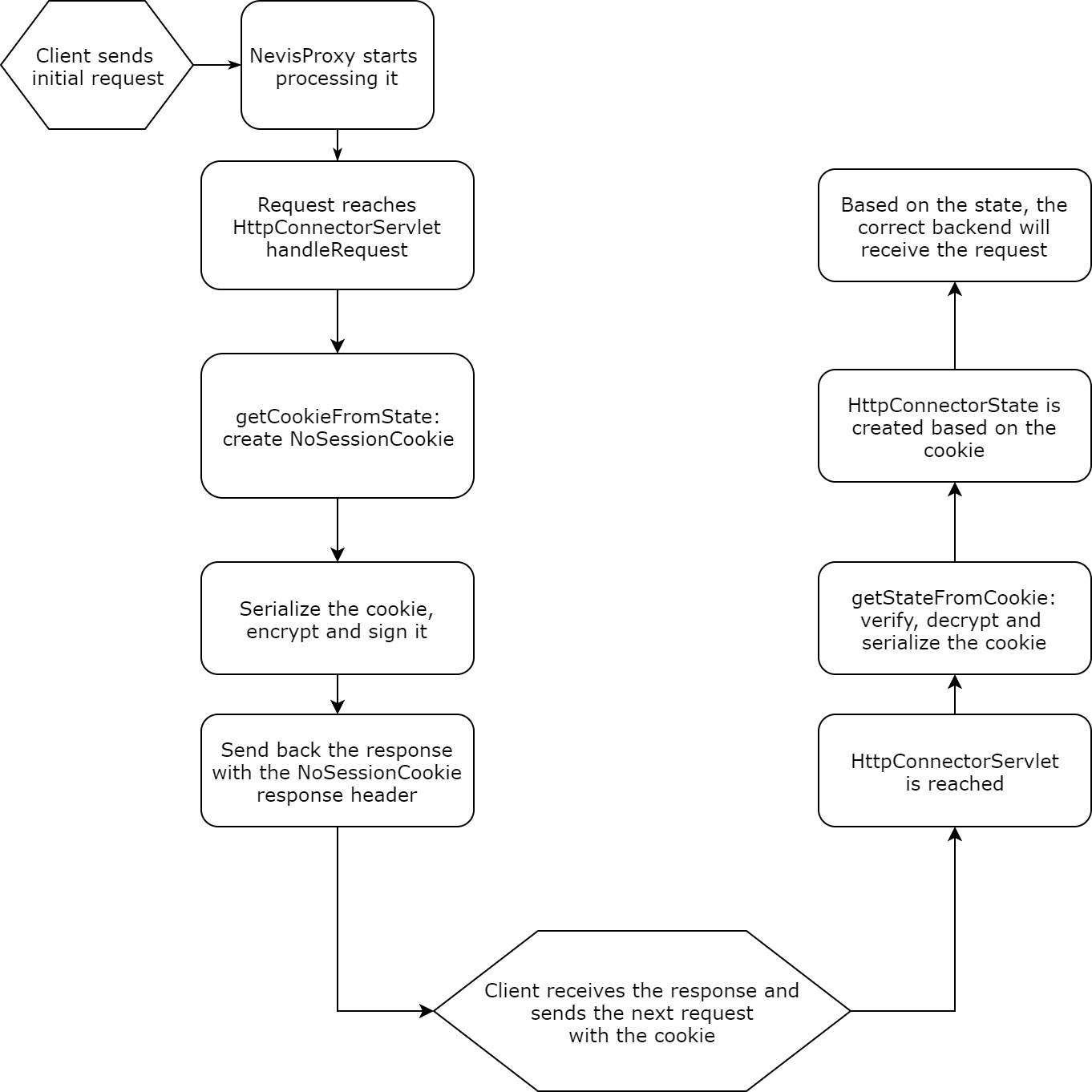
You configure the behavior of the NoSessionCookie feature with the following ResourceManager.NoSessionCookie.* attributes of the HttpConnectorServlet:
| Name | Type, Usage Constraints, Defaults | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ResourceManager.NoSessionCookie | boolean; optional, advanced | The information which backend has been used will not be saved within the HTTP session but within a cookie sent to the client. This facilitates sticky load balancing without sessions within nevisProxy. This parameter cannot be set to "true" when SSLCache is set to "session", and either DisableBindingStatusCode or KeepAlive.ByClient is enabled. |
| ResourceManager.NoSessionCookie.CookieName | string; optional, advanced | The name of the cookie if the parameter ResourceManager.NoSessionCookie is enabled. |
| ResourceManager.NoSessionCookie.CookieDomain | string; optional, advanced | The domain of the cookie if the parameter ResourceManager.NoSessionCookie is enabled. |
| ResourceManager.NoSessionCookie.CookiePath | string; optional, advanced | The path of the cookie if the parameter ResourceManager.NoSessionCookie is enabled. |
| ResourceManager.NoSessionCookie.CookieHttpOnly | boolean; optional, advanced | If set to "true", the HttpOnly attribute is added to the cookie, if the parameter ResourceManager.NoSessionCookie is enabled. Be aware that the HttpOnly flag might be overwritten by Navajo. For details, refer to the description of the attribute cookieHttpOnly in the table: UserAgent attributes. |
| ResourceManager.NoSessionCookie.CookieSecure | boolean; optional, advanced; secure default: true | If set to "true", the ResourceManager.NoSessionCookie will have the secure attribute set. |
| ResourceManager.NoSessionCookie.EncryptionKey | string; optional, advanced | Symmetric encryption key used to encrypt the information within the cookie (the stickiness information). |