Side-by-side Deployment
EXPERIMENTAL FEATURE
Overview
Do you want to mitigate the risk in application deployment and make sure that your application is in good quality before it is rolled out to production?
The Kubernetes side-by-side deployment supports you in this regard. With this deployment strategy, you can make frequent delivery and deployment, and release a better quality application to production.
The side-by-side deployment strategy reduces risks in the application release as it allows you to release to a smaller subset of users first. You deploy new features and configuration into the active production as a secondary release that is running side by side to the previous release (aka the primary version). Additionally, you can manage and control the traffic between these two versions. Traffic that meets certain parameter sets, such as header and cookie settings, is directed to the new version, whereas the rest of the users still accesses the previous version. This ensures zero downtime to the users during a deployment. It also gives the QA team enough time and flexibility to test and monitor the deployment. Once the quality is approved, you can fully roll out the new version to production.
For more advice regarding the side-by-side deployment, read the chapter Recommendations and Limitations.
How it Works
The primary and secondary deployments are defined as follows:
- The primary deployment is a productive deployment available for all users.
- The secondary deployment is a deployment added next to the primary one and accessible only to a limited number of users. It is created for testing purposes. Based on the test results, this deployment can be promoted or rolled back. The traffic routing to this deployment is based on the Header and Cookie of the request.
Both primary and secondary deployments are deployed in the same inventory and run inside the same namespace. No additional installation or setup is needed, the [Kubernetes-Based Installation]( is enough.
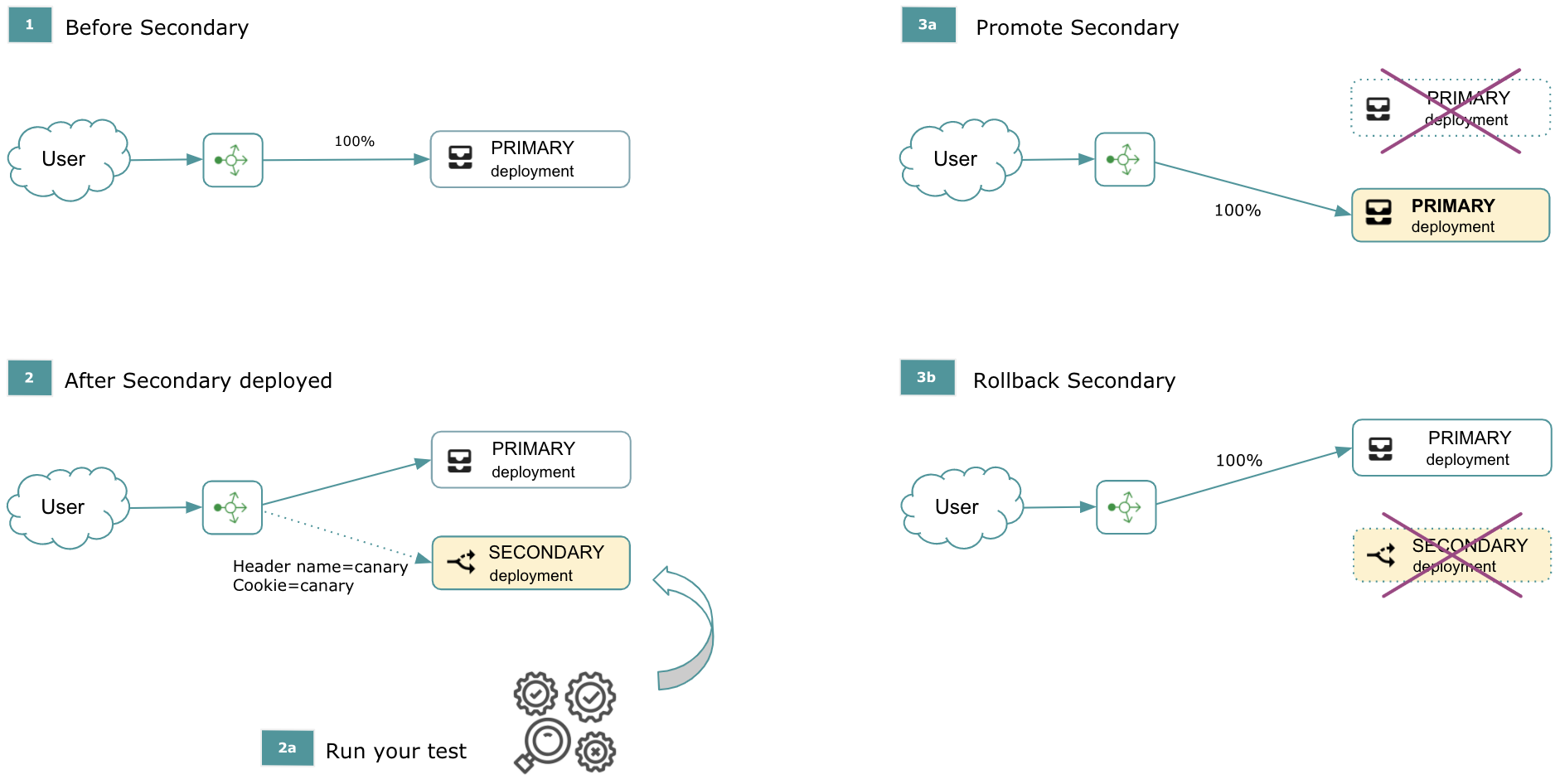
The figure below shows how the traffic is split among the installed versions (the numbers in the figure correspond with the numbers in the following list):
- Your current setup - 100% traffic is going to your primary version.
- You deploy a secondary version and have set up at least one of the required routing parameters, such as a Header name and/or Cookie name. The traffic will be directed to the secondary version based on a routing parameter. You will be able to test and monitor your deployment, and afterwards to decide to rollback or promote this deployment to production.
- You will either promote or rollback the secondary deployment:
- In case of promotion, the secondary deployment will become your primary deployment. The previous primary version will be removed. 100% of your traffic will go to your newly promoted primary version.
- In case of a rollback, the secondary deployment will be removed. 100% of your traffic keeps going to your primary version.
Deploy as Secondary (Side-by-Side)
When you create a secondary deployment, make sure that you deploy all your projects as secondary. This is necessary, because the moment you promote the secondary deployment, you replace the entire primary deployment with the secondary one. The components between the primary and secondary versions cannot connect to each other.
To make a secondary deployment, there must already be a primary version deployed to the selected Kubernetes inventory.
Perform the following steps to create a side-by-side deployment:
- Open the Deployment Wizard by clicking on the Deploy button, or on the Deploy as Secondary button in Kubernetes Status screen.
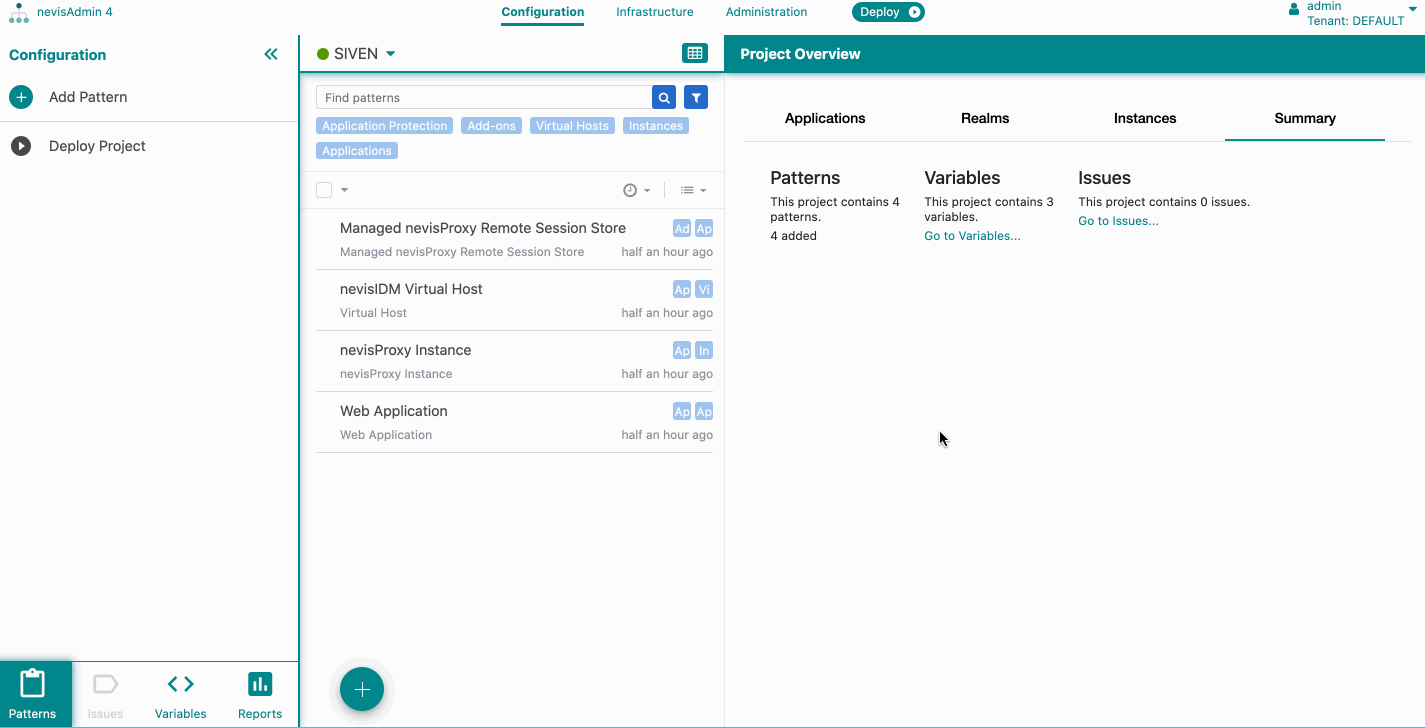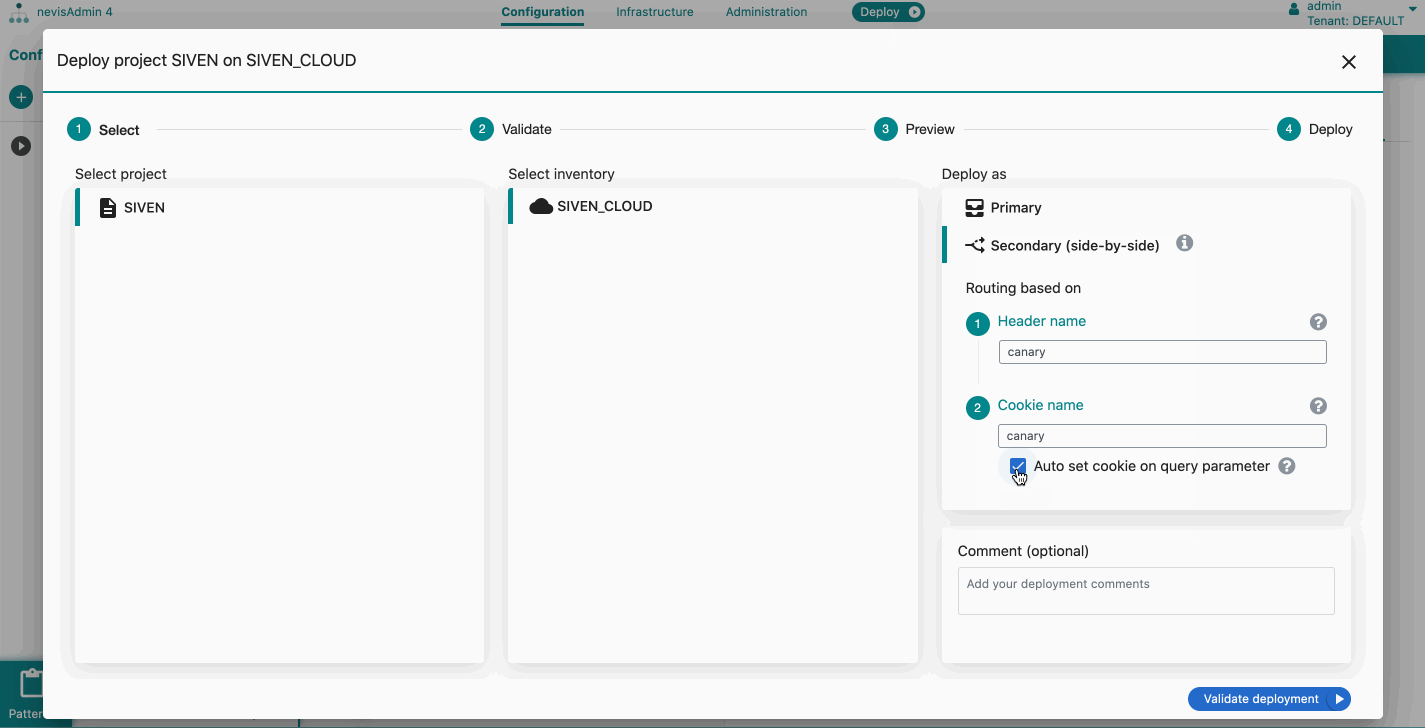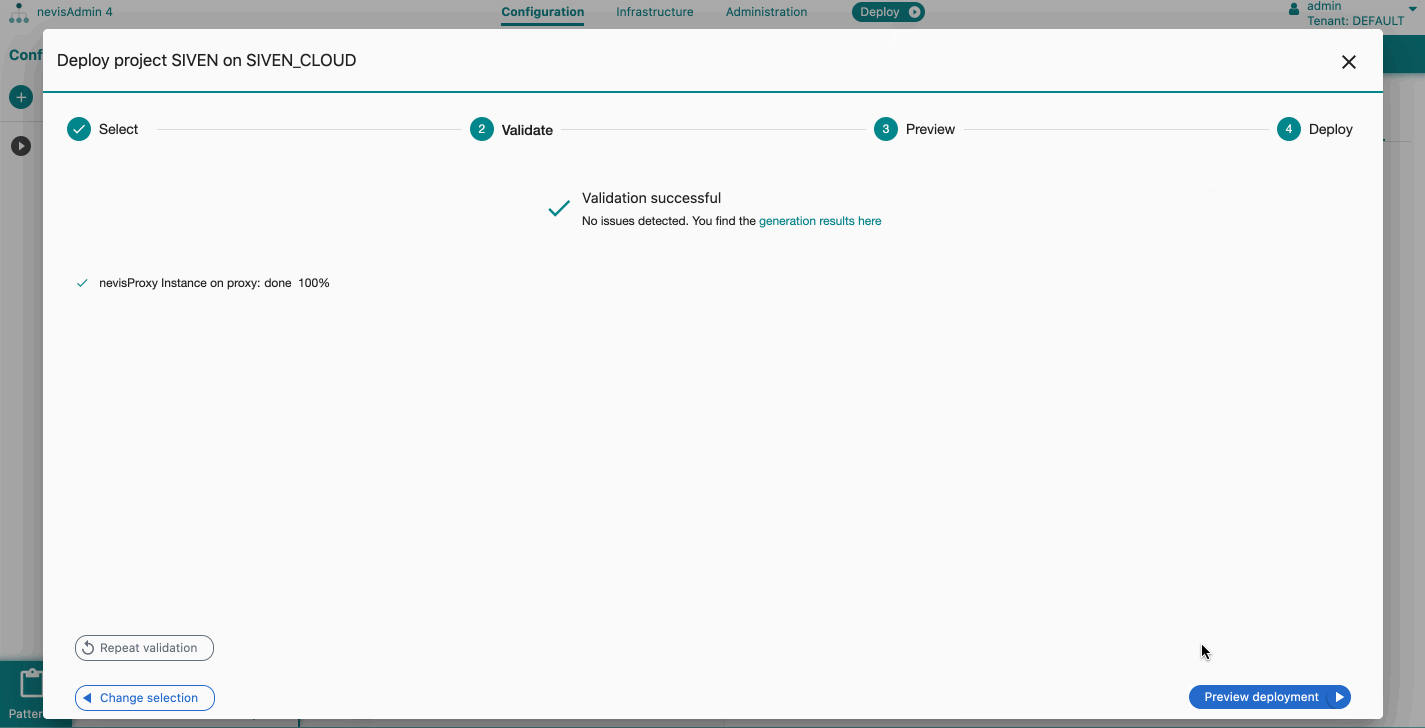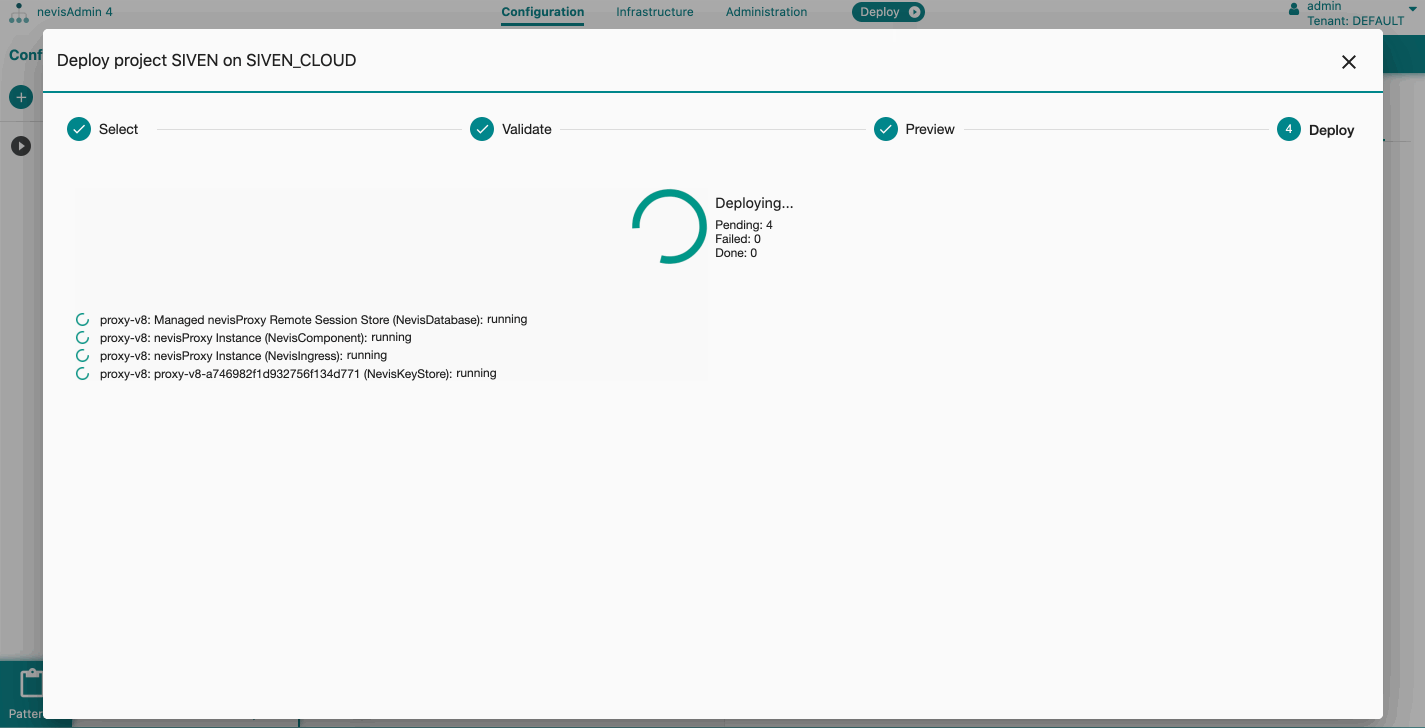
- Select your project, the Kubernetes inventory and the Secondary (side-by-side) option.
- Define the routing parameters such as the Header name and/or Cookie name (or leave the default values as is). The routing to the secondary deployment will be based on these parameters. At least one of the parameters must be set. Tick the Auto-set cookie checkbox to set the routing based on a URL including a query parameter (see further details below).
Note that the sequence of the fields matter: The system first checks for the Header name and then in the Cookie header.If the Header name is found, the Cookie name is skipped.Header nameThe system checks if the request header contains the defined header name. If yes, it checks for the value of the header:
- If the value is "always", the traffic goes to the secondary version.
- If the value is "never", the traffic never goes to the secondary version.
- In case of all other values, the traffic goes to the primary version.
Note that the key-value pair and regex are not supported in this release. However, this is planned for the future.Cookie nameThe system checks if the request header contains the defined cookie name. If yes, it checks for the value of the cookie:
If the value is "always", the traffic goes to the secondary version.
If the value is "never", the traffic never goes to the secondary version.
In case of all other values, the traffic goes to the primary version.
Auto-set cookie on query parameterEnable this checkbox to set up the routing to the secondary deployment with a URL. For this, first define the Header nameand Cookie name. After the first request, the cookie will be added automatically based on the given query parameter. Here are sample URLs including a query parameter:
URL to enable routing to the secondary deployment:
<yourURL>/?canary=always, where "canary" is the cookie name.URL to disable routing to the secondary deployment:
<yourURL>/?canary=never, where "canary" is the cookie name.
- You may add a comment to the deployment.
- Click on Validate deployment.
- From this step on, the flow is the same as for the normal deployment ").
Note that the routing information you provide during the deployment creation is applied by the NevisIngressresources, which are generated by the nevisProxy instances. Therefore, if you wish to change the Header name and Cookie namefields set for the environment, you have to redeploy the projects containing these instances.
This release does not support traffic allocation based on a user percentage. However, this feature is planned for the future.
The following movie shows how to create a secondary deployment:
View Active Deployments
- Select the Infrastructuretab.
- Select a Kubernetes inventory from the dropdown.
- Click on the Kubernetes Status item in the Navigation menu on the bottom of the sidebar.
The Kubernetes Status item is available only for Kubernetes inventories.
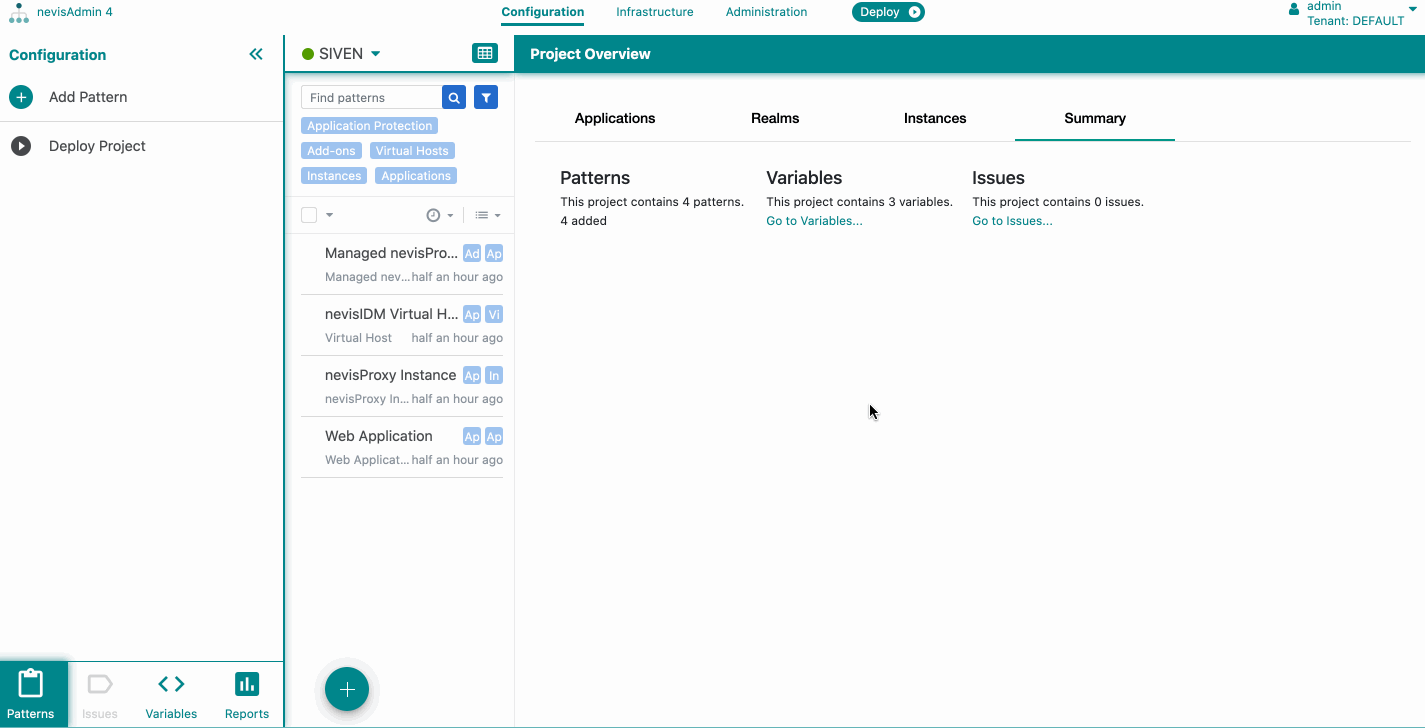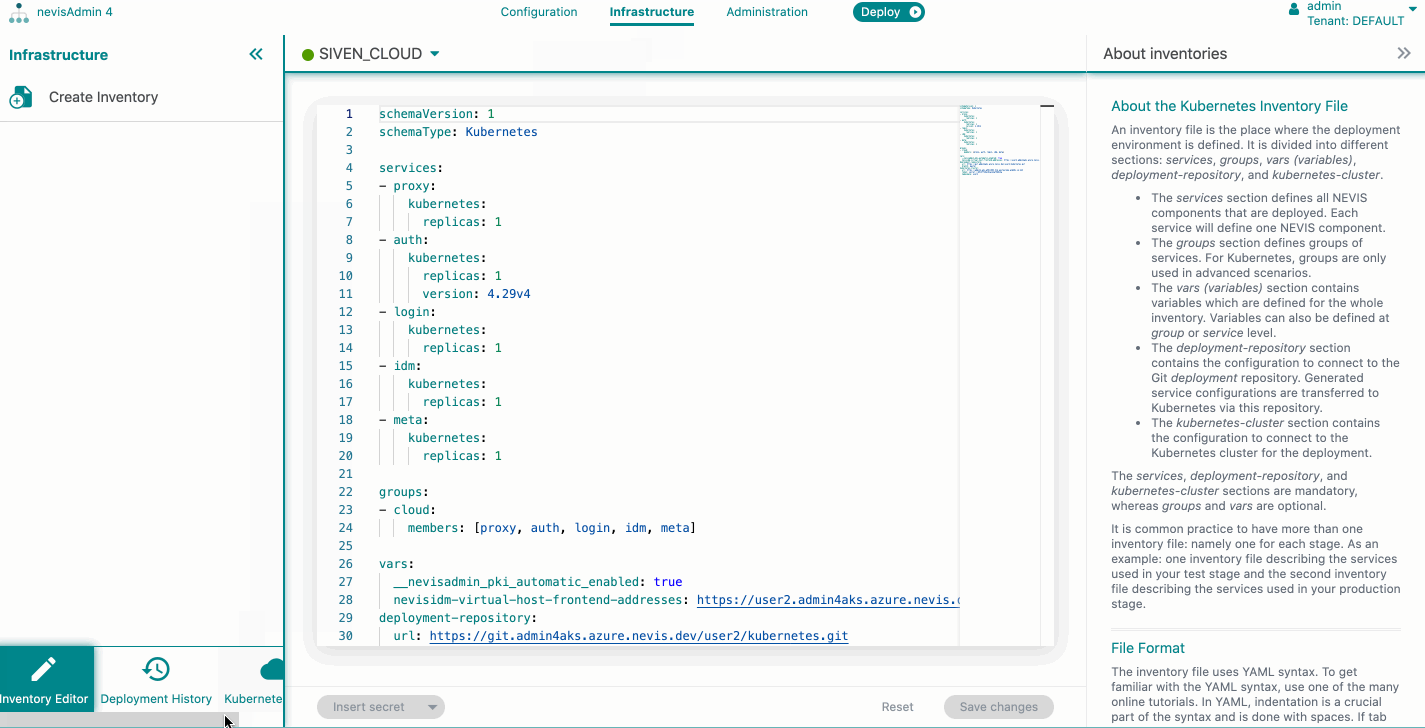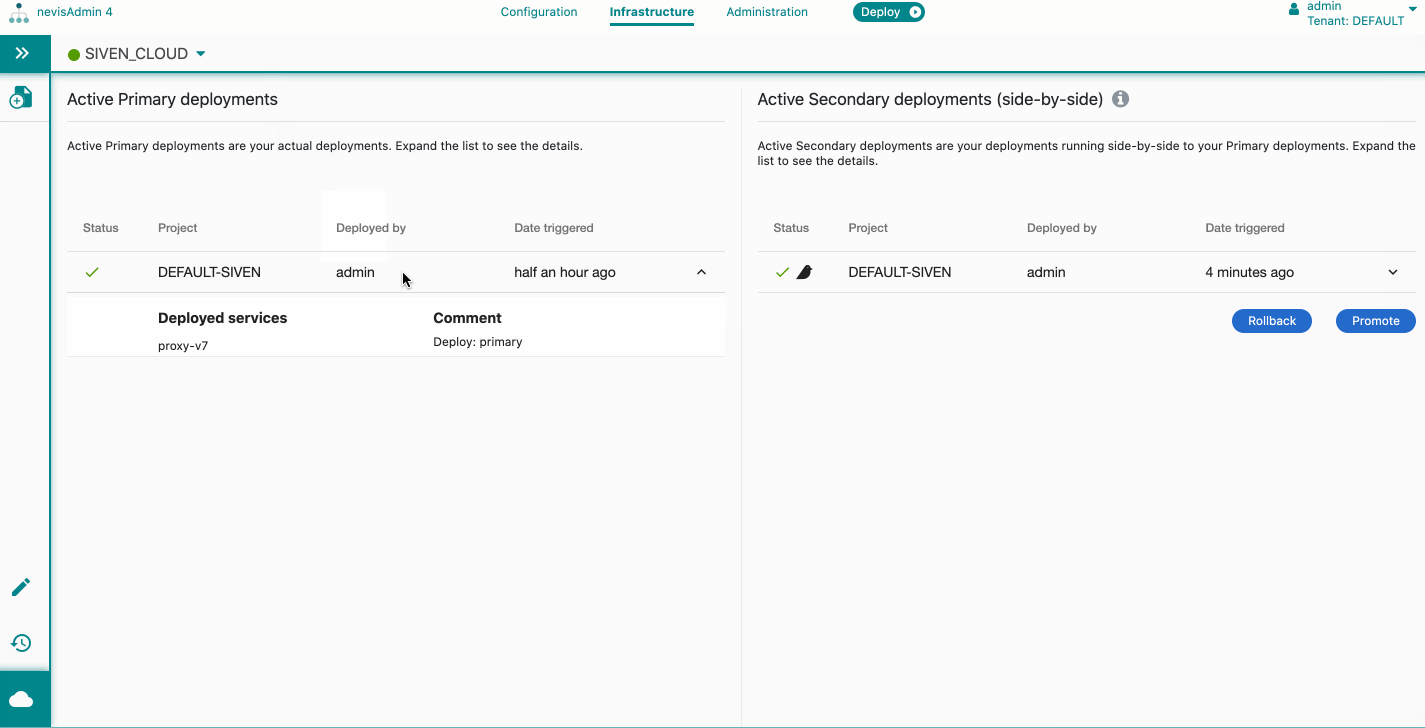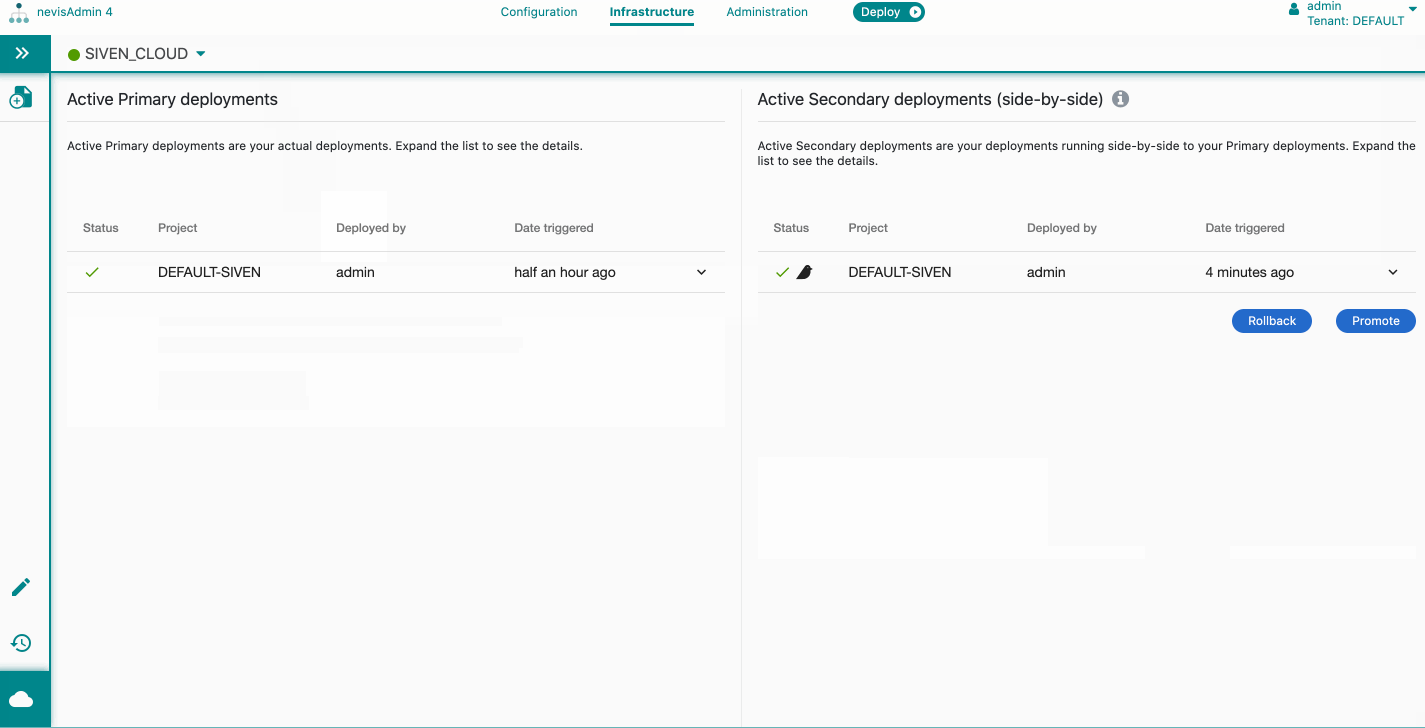
The Kubernetes Statusscreen opens. It consists of two sections:
- Active Primary deployments
- Active Secondary (side-by-side)
To view further details about a deployment, click its entry in the list. The following sections are shown per deployment entry:
- Deployed services The list of deployed services, with the version number (e.g., proxy-v2). The version number is incremental.
Note that the version number does not indicate the version of the component. It is rather a technical indicator to differentiate between secondary and primary deployments. The field is available for deployments done in nevisAdmin 4 version 4.9.
- Deployment repository git tagGit tag of the generated configuration. To copy the tag, click on the copy icon.
The field is available for deployments done in nevisAdmin 4 version 4.9.
- CommentShows the comment that you entered during the deployment and/or promotion or rollback.
- Secondary (side-by-side) deploymentShows the routing information for the secondary deployments.
The following movie shows how to view active deployments:
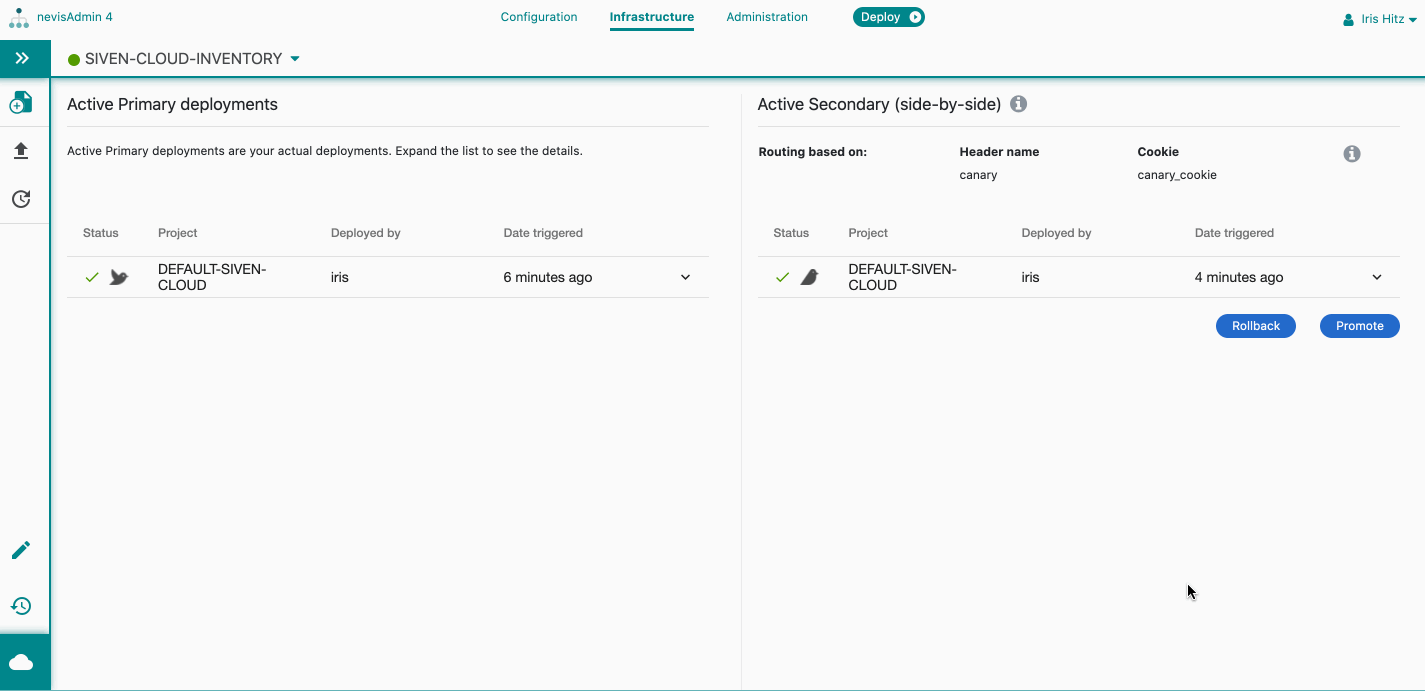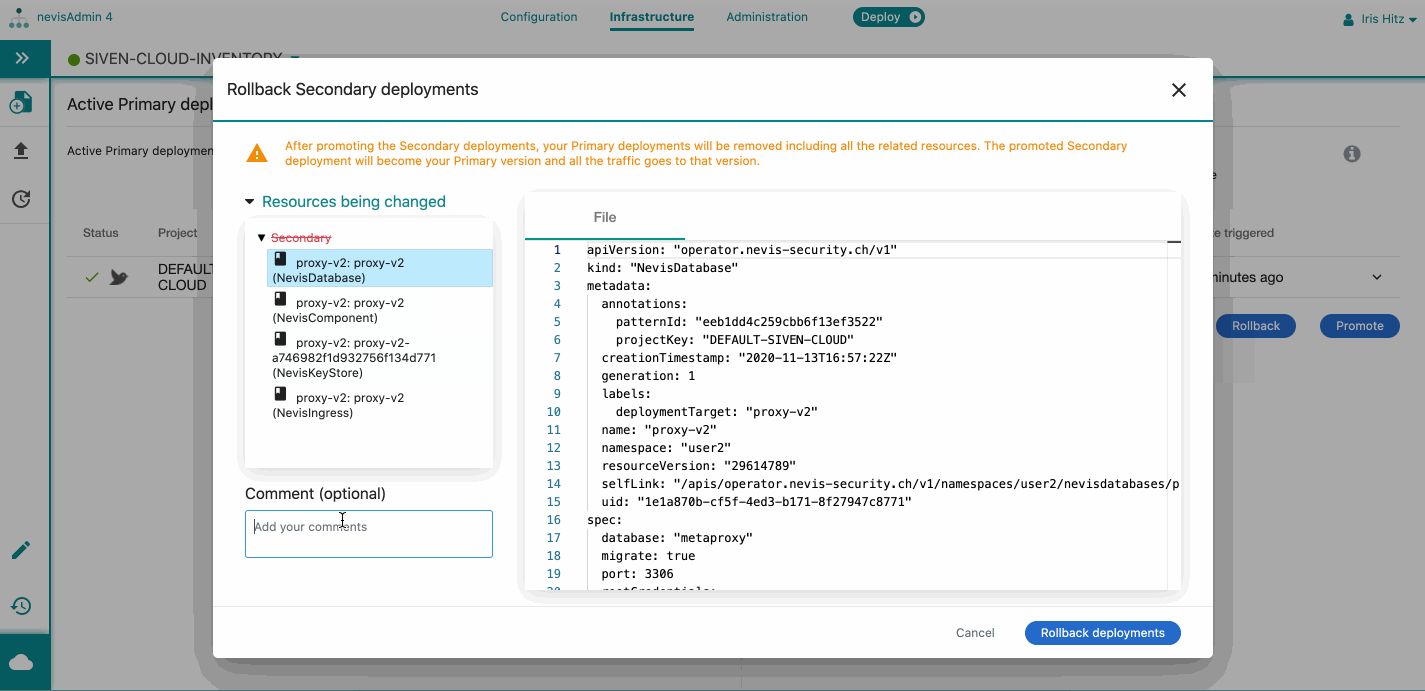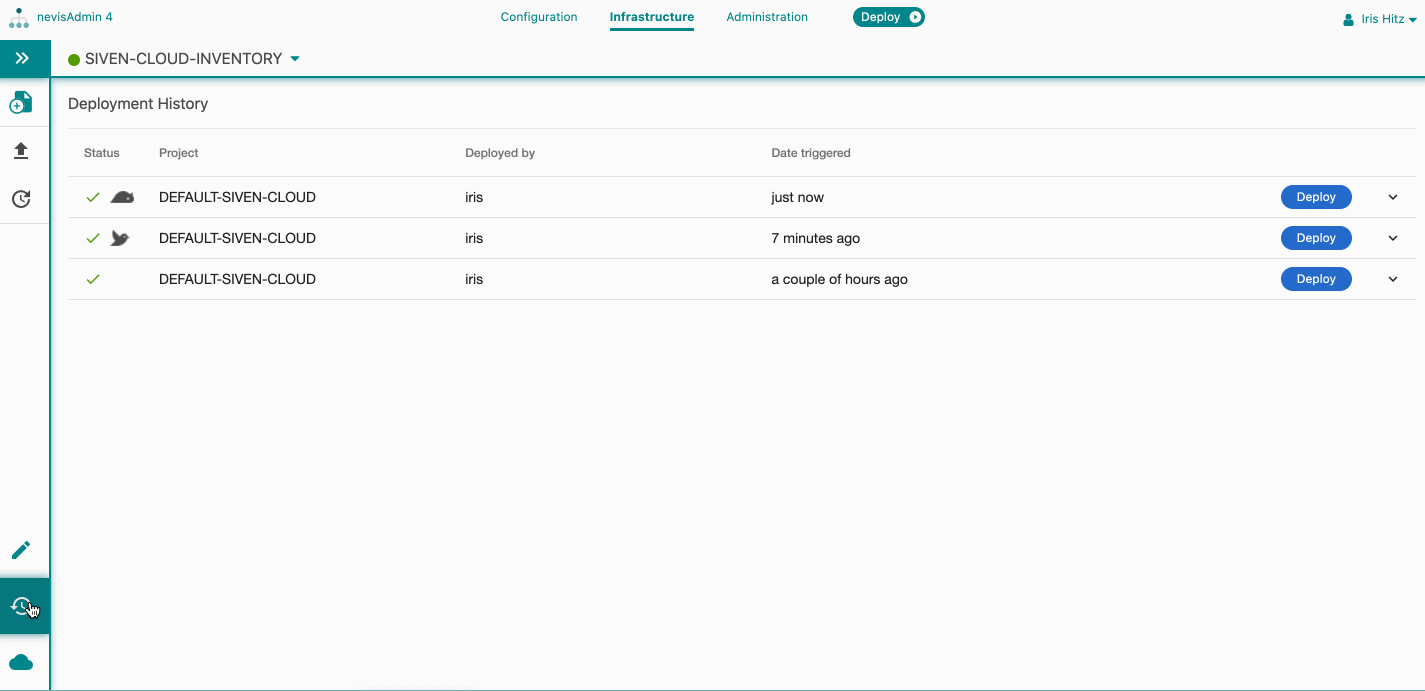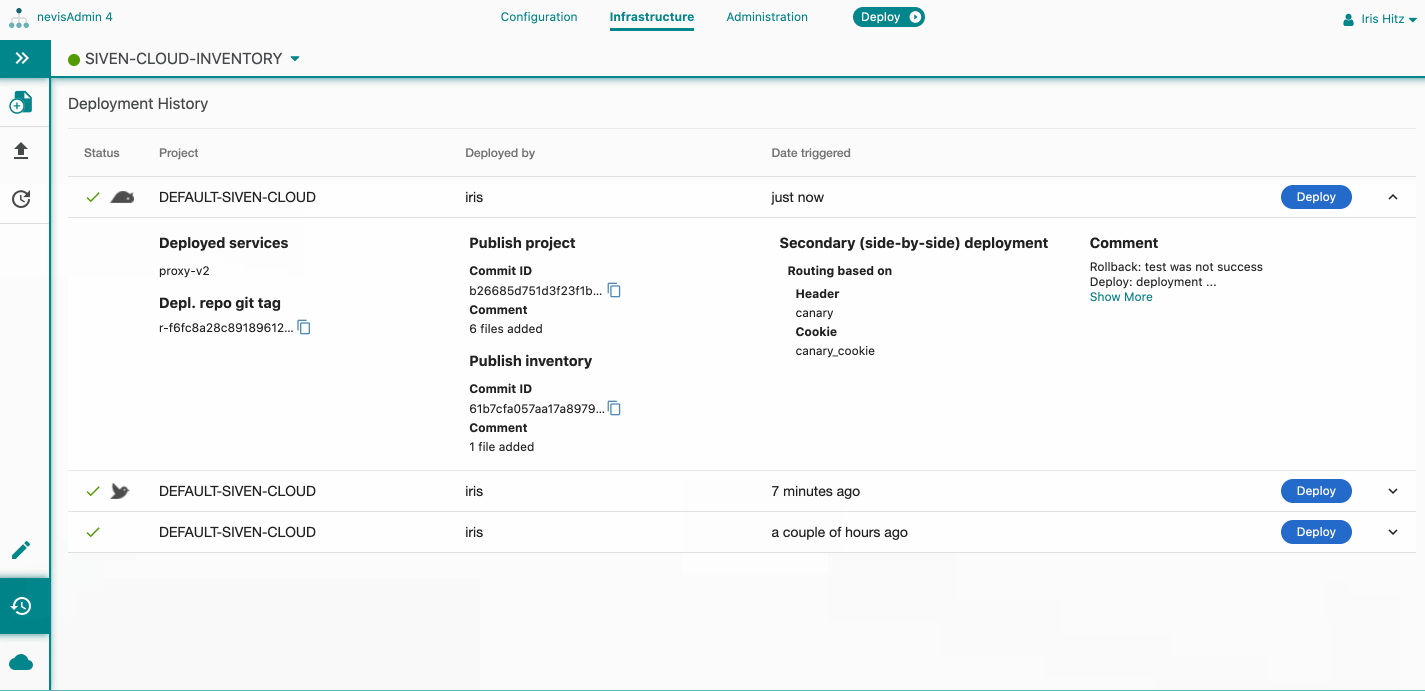
Promote Secondary Deployments
When promoting your secondary deployments, the following happens:
- The secondary deployments become your primary deployments, and all traffic will go to these new primary deployments.
- The previous primary deployments are deleted.
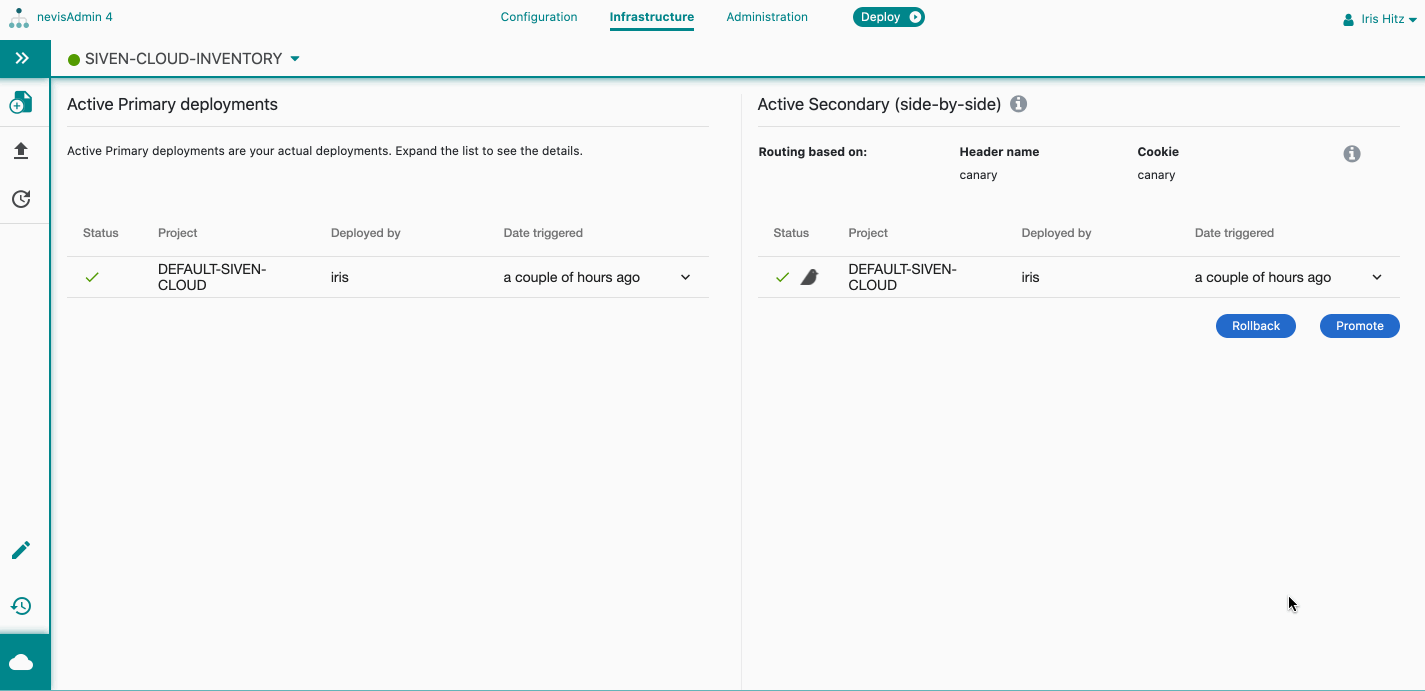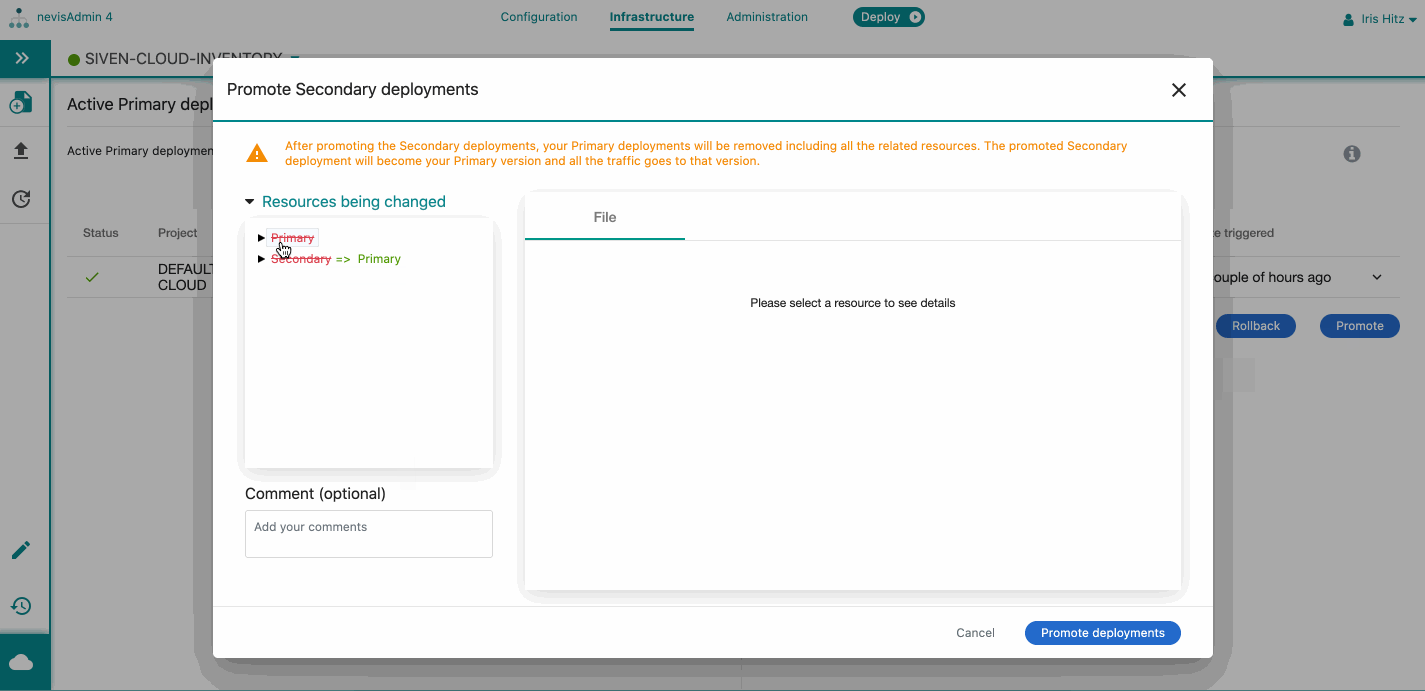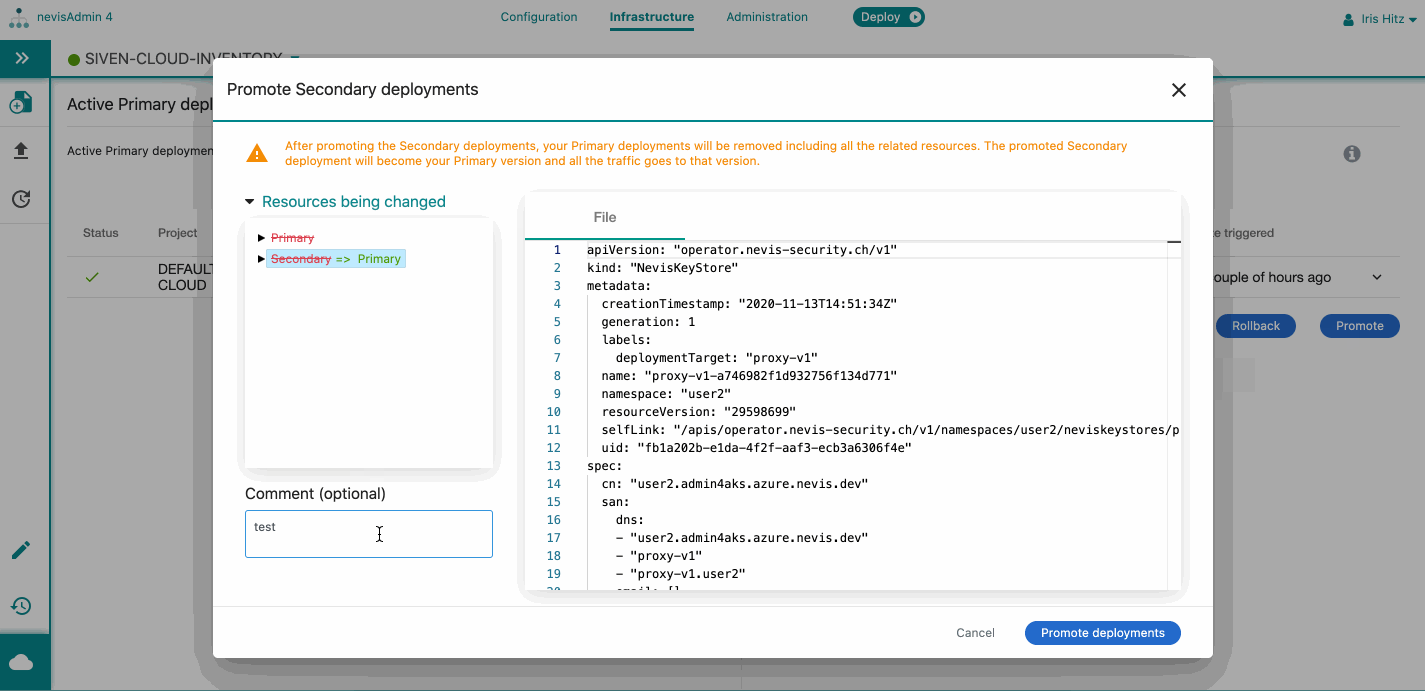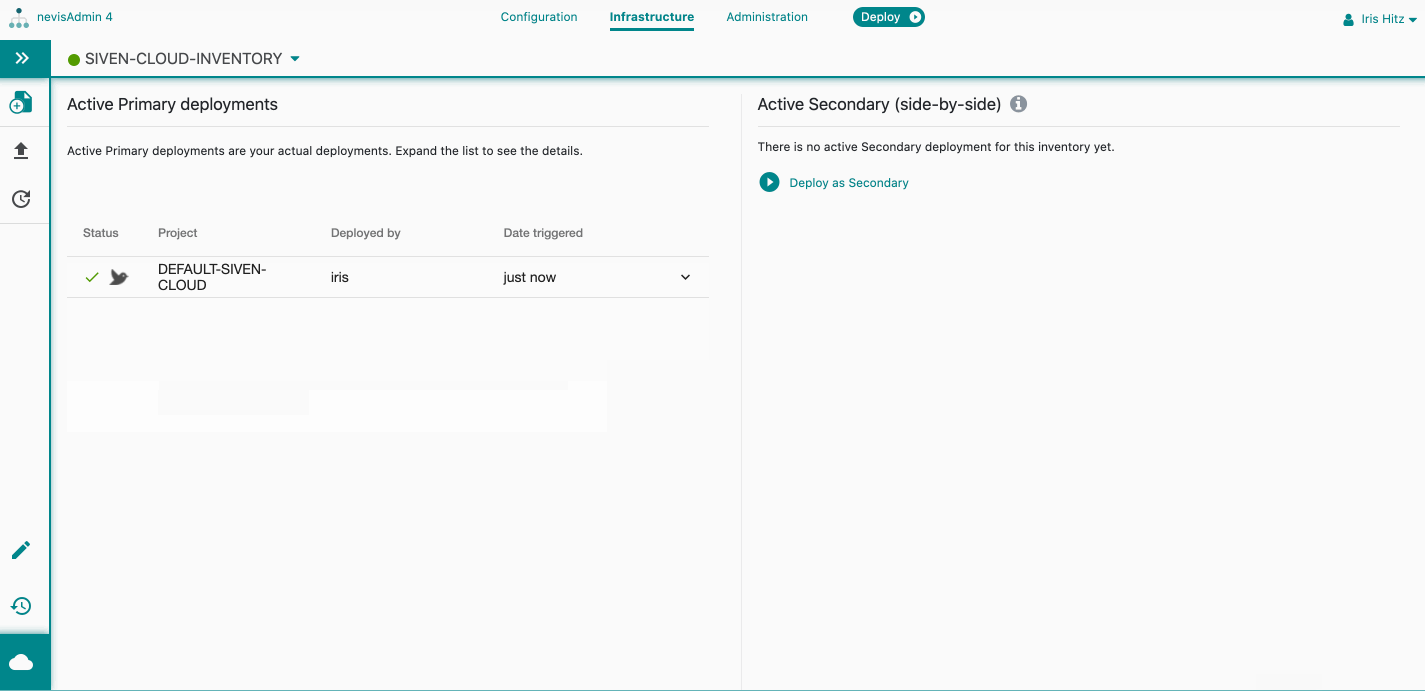
Take the following steps to promote the secondary deployments:
- Open the Kubernetes Statusscreen.
- Click on Promotebutton under the Active**Secondary deployments (side-by-side) list.
- The Promote Secondary deployments dialog screen opens.
- You can check the resources that will be changed due to the promotion. Expand the resources list to see the details. Note that
- The primary version and related resources will be deleted.
- The secondary version and related resources will become the primary after the promotion.
- You can add a comment/reason to your promotion.
- Click on Promote deployments.
- All the secondary deployments in the Active**Secondary deployments (side-by-side) list are promoted to be the primary version and visible in the Active Primary deployments list.
If promoting the secondary deployment fails, just retry. Do not rollback the primary deployment. This is because the primary deployment might have been affected due to the promotion, such as damaged or removed. If the promotion of the secondary deployment fails again, deploy everything from the beginning.
The following movie shows how to promote secondary deployments:
Rollback Secondary Deployments
You can rollback your secondary deployments. This will,
- Remove the secondary deployments and all the related resources.
- Not affect the primary deployments. The traffic will continue to go to them.
Take the following steps to rollback the secondary deployments:
- Open the Kubernetes Statusscreen.
- Click on Rollbackunder the Active**Secondary deployments (side-by-side) list.
- The Rollback Secondary deployments dialog opens.
- You can check the resources that will be changed due to the promotion. Expand the resources list to see the details. Note that
- The secondary version and related resources will be deleted.
- You can add a comment/reason to your promotion.
- Click on Rollback deployments.
- All the secondary deployments in the Active**Secondary deployments (side-by-side) list are removed, but can be found in the Deployment History screen.
To access the Deployment History screen, click on Deployment History in the Navigation menu in the sidebar of the Infrastructure tab.
If rolling back the secondary deployment fails, retry. If the rolling back fails again, re-deploy all secondary deployments from the beginning.
The following movie shows how to rollback secondary deployments:
Deployment History
You can view the secondary deployment history in the Deployment History screen. See further details in the chapter Deployment History and Rollback.