Technical architecture
To provide FIDO2 authentication, Nevis FIDO2 relies on several Nevis components which contribute to the overall solution. The central components use are depicted in the following figure.
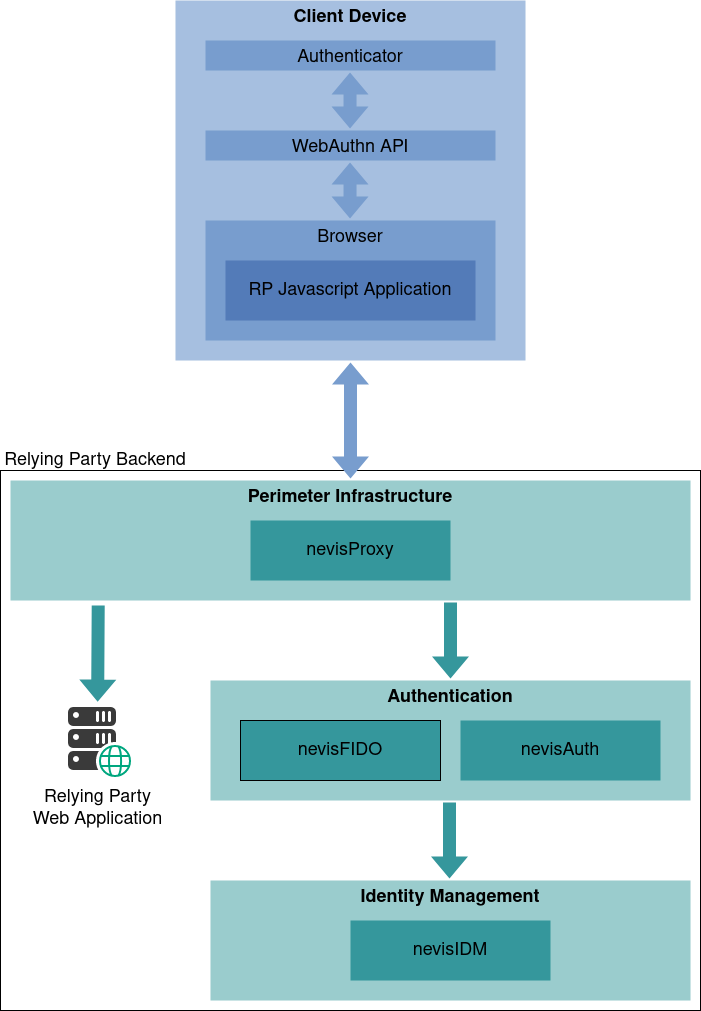
Within the Nevis architecture, nevisFIDO acts as a service to implement the FIDO2 specification standard.
The nevisFIDO component tightly integrates with other Nevis components to deliver the complete FIDO2 authentication feature. In the sections that follow, we highlight briefly the functions of the subsystems that work together to ultimately deliver FIDO2 authentication to the client browser.
Client Device
The client device represents the physical device owned by a user, e.g. a laptop. To use and benefit from Nevis FIDO2 Authentication.
RP JavaScript application
The relying party JavaScript application is used to orchestrate the FIDO2 registration and authentication operations by on one hand interacting with the authenticators via the WebAuthn API and on the other hand with the backend server using the FIDO2 protocol.
WebAuthn API
The WebAuthn API is used to let the browser interact with the authenticator provided by the client device.
Authenticator
Credentials belonging to the user are managed by an authenticator. The WebAuthn Relying Party interacts with it through the client device by using the Relying Party JavaScript Application, which internally relies on the WebAuthn API provided by the client browser.
Relying party backend
The relying party backend characterizes the group of components which in combination act together as the Relying Party backend of a FIDO2 Relying Party client. In the context of FIDO2, communication between a FIDO Client and a FIDO Server always occur via the Relying Party JavaScript Application and Nevis backend. In Nevis FIDO2, this backend includes the necessary Nevis components described below and the protected backend entity named Web application in the Nevis FIDO2 architecture figure.
Perimeter infrastructure
nevisProxy
Towards the client-facing edge of the system, the nevisProxy component serves as the perimeter server. It's able to protect web applications from unauthenticated access and ensures that authentication takes place before requests are passed to those web applications. In Nevis FIDO2, nevisProxy is configured to accept requests according to the FIDO2 protocol and forwards them to the authentication subsystem. As in all Nevis setups, additional functions of nevisProxy are web application firewall, session management (single sign-on), and reverse proxy functionality like routing and rerouting of requests to downstream components. In Nevis FIDO2, nevisProxy will route FIDO2 HTTP requests to nevisAuth, which forwards them to nevisFIDO. The latter two form the authentication subsystem.
Authentication
nevisFIDO
At the core of the system, the nevisFIDO component is a specification-compliant implementation of a FIDO2 Server. As such, it handles FIDO2 protocol level processing and provides support for the FIDO2 ceremonies (registration, authentication). It is the nevisFIDO component that ultimately performs cryptographic operations like signature verification and thus establishes the authenticity of a user. For persistent storage, nevisFIDO relies on the IAM component nevisIDM.
nevisAuth
Participating in the Nevis FIDO2 solution, nevisAuth acts as bridge between the FIDO2 Client and the FIDO2 Server, making up for the Nevis authentication specific details nevisFIDO cannot account for. As usual, nevisAuth is used to implement sophisticated authentication flows, including flows that rely on IAM provided by nevisIDM. It does not deal with FIDO2 protocol level messages but dispatches them to nevisFIDO, delegating the authentication to that component.
Identity management
nevisIDM
In the context of Nevis Mobile Authentication, nevisIDM is acting as a persistent storage of FIDO2 authenticator credentials. With every user-performed registration on a client device that takes part in Nevis FIDO2 authentication, cryptographic information such as an authenticator's public key are stored in nevisIDM.
Third-party backend
The third party backend characterizes components that are not part of either the Relying Party Backend or the Client. Usually these components are located outside the managed infrastructure.