SAML 2.0 Login
SP-Initiated Authentication
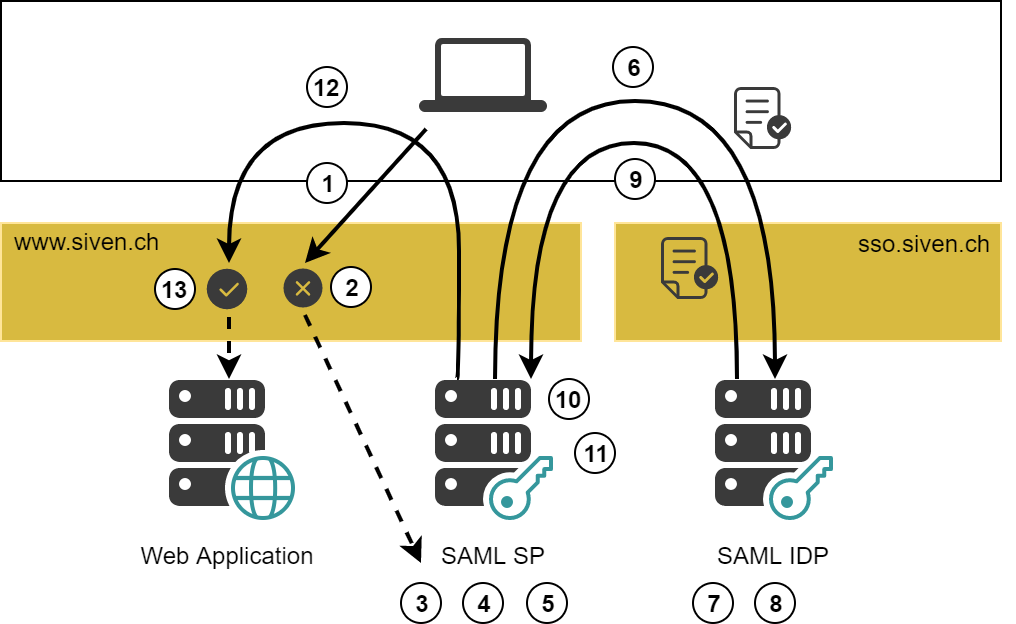
SP-initiated SAML authentication works as follows (the numbers of the steps below correspond with the numbers in the figure above):
- The user wants to access the web application www.siven.ch:
- The web application is behind a nevisProxy virtual host and protected by a SAML SP Realm.
- The user uses a browser-based client.
- As there is no authenticated session, access to the application is blocked.
- Session tracking is based on a session cookie.
- Authentication is enforced by nevisProxy.
- The request is forwarded to nevisAuth, which acts as SP and initiates the SAML flow.
- The SP checks if the session has been expired.
- This check is optional and can be enabled in the SAML SP Realm pattern (Session Expiration tab).
- The SAML SP Realm pattern provides different strategies on how to handle expired sessions. Each strategy corresponds with a field in the Session Expiration tab:
- Logout Reminder: Renders a page that reminds the user to log out in the future.
- Timeout Page: Renders a page that informs about the termination of the session due to timeout.
- Session Expiration Redirect: Redirects to a configurable URL (for example, a hosted resource or the URL of the IDP to trigger IDP-initiated authentication).
- The SP can also execute an optional custom pre-processing step.
- You configure this step in the Custom Pre-Processing field of the SAML SP Realm pattern (Advanced Settings tab). Check the pattern's Help section for further information about this advanced feature.
- The SP now determines which SAML IDP to invoke.
- This step is not relevant when only one IDP is configured.
- The IDP is selected based on a selection expression. You configure this expression in the SAML IDP Connector pattern (Selection Expression field, Advanced Settings tab). Check the pattern's Help section for examples.
- The SP returns an AuthnRequest.
- The AuthnRequest contains the Issuer of the SP and is signed with the SAML Signer of the SP.
- The SP stores the current URL (of the application) in a RelayState parameter.
- The SAML standard demands that the IDP returns this RelayState parameter unchanged.
- The browser is instructed to send AuthnRequest and RelayState to the IDP. How these parameters are transmitted can be configured in the SAML IDP Connector pattern (Binding: Outbound field, Basic Settings tab):
- POST-binding ("http-post"): Self-submitting form. This is the default setting.
- Redirect-binding ("http-redirect"): Using query parameters and a 302 redirect.
- The IDP consumes the AuthnRequest.
- The IDP first extracts the Issuer from the AuthnRequest and dispatches the request into the correct IdentityProviderState.
- Each SAML SP Connector pattern generates one IdentityProviderState.
- The IdentityProviderState validates the signature of the AuthnRequest.
- If the signature is not valid, then a standard SAML error response is returned.
- The IDP first extracts the Issuer from the AuthnRequest and dispatches the request into the correct IdentityProviderState.
- If the user has no authenticated session on the IDP he has to log in first.
- The authentication flow is defined by the Authentication Realm pattern assigned to the SAML IDP pattern.
- Once the session is authenticated, the SAML IDP produces a SAML Response.
- The Response is sent to the AssertionConsumerServiceURL that has been extracted from the AuthnRequest.
- If no AssertionConsumerServiceURL is found, then the URL defined in the SAML SP Connector pattern is used.
- The SP consumes the Response:
- Based on the Issuer of the Response the corresponding ServiceProviderState for this IDP is selected.
- Each SAML IDP Connector pattern generates one ServiceProviderState.
- The ServiceProviderState validates the signature of the Response.
- If the Response contains an AudienceRestriction then it has to match the current URL.
- The SP can execute an optional post-processing flow.
- You configure this flow in the Post-Processing Flow field of the SAML SP Realm pattern (Advanced Settings tab). Check the pattern's Help section for further information about this advanced feature.
- The SP declares the authentication as done and redirects back to the web application.
- The URL of the application is taken from the RelayState parameter.
- As there is an authenticated session now, nevisProxy allows the user to access the application.
- If an Application Access Token is assigned to the web application, the SAML SP is invoked again to produce that token.
- If an Authorization Policy is assigned that demands a higher authentication level, a session upgrade may be performed. See the chapter SAML Flow for Session Upgrade for details.